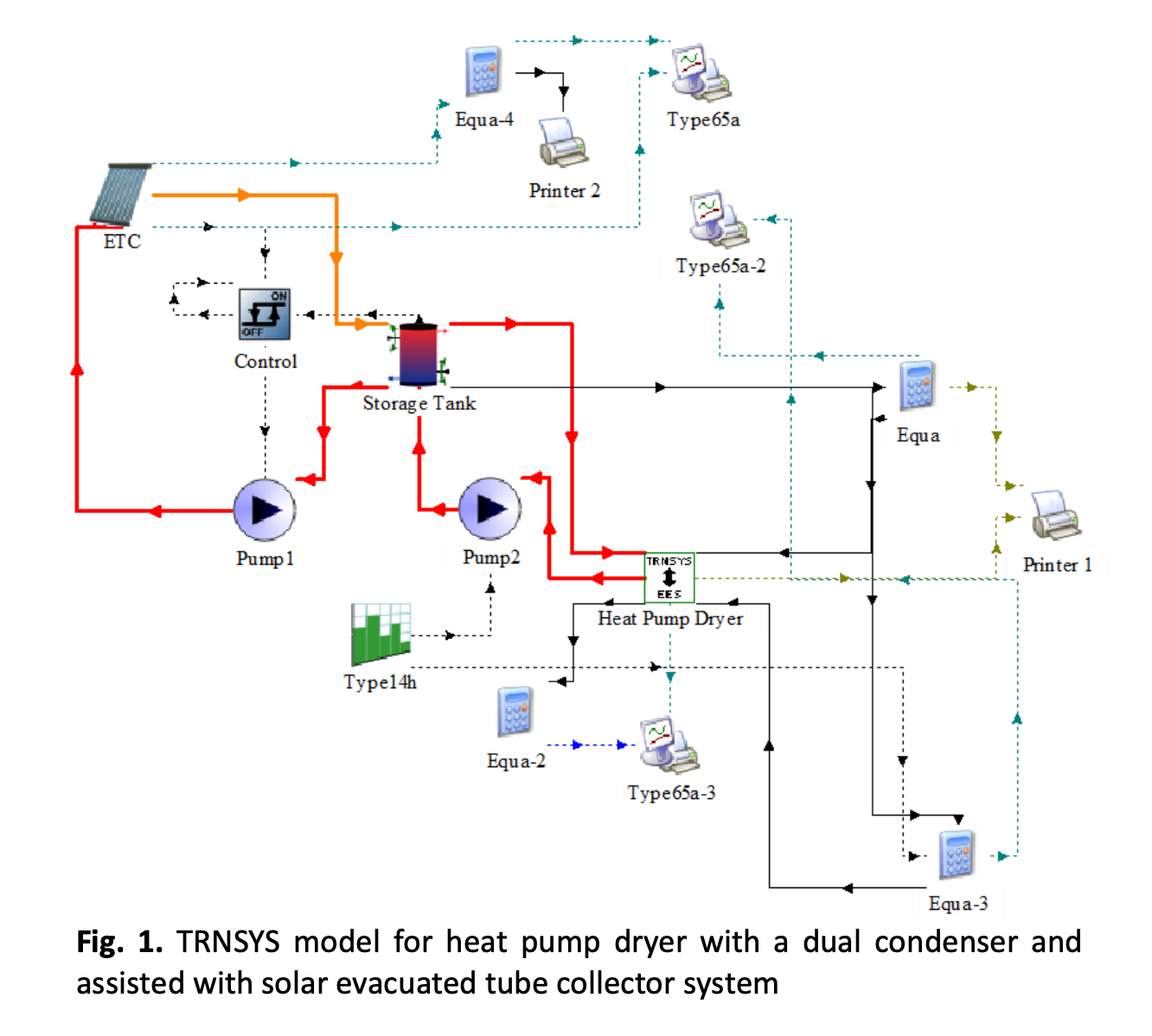
Performance Analysis of Solar Assisted Heat Pump Drying System with Dual Condensers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.99.1.134148Keywords:
Heat pump, dryer, dual condensers, evacuated tubes, TRNSYS, EES simulationAbstract
The main components of the dual condenser solar-assisted heat pump (SAHP)drying include the solar collector, evaporator, compressor, fan coil, twin condensers, expansion valve, and drying chamber. The solar drying process was assisted by a heat pump, and the optimal efficiency was determined by heating and dehumidifying the air, and recirculating the air that has been heated. The efficiency of the heat pump system was assessed by its coefficient of performance (COP), which is the percentage of the actual heat delivered by the heat pump to the total electrical power necessary to operate the heat pump. The average temperature of the drying chamber reached a temperature of 60 °C with a relative humidity of around 70%, and the system's COP was 5.546 with no contribution from solar energy or at no solar fraction (SF = 0). The same conditions in the drying chamber can be achieved at solar faction or SF = 0.83, with COP increased to 12.7.
Downloads