Performance Analysis of Flat Plate Base-Thermal Cell Absorber (FPBTCA): Low Thickness Design
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.96.2.122133Keywords:
Flat plate solar collector, thermal cell absorber, solar thermal collectorAbstract
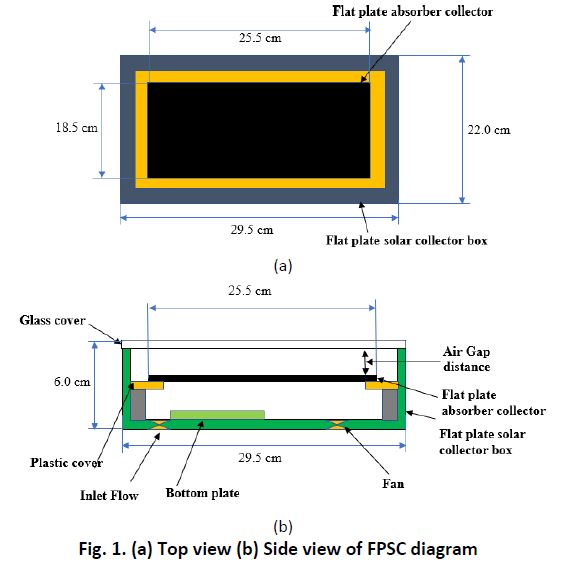
Research to improve flat plate solar collector performance such as design and material used continuously developed. This paper's objective is to analyze the performance of the thermal cell absorber attached to a flat plate absorber collector (FPBTCA) through a low thickness design. It will produce a lightweight and portable collector application with efficient temperature conversion duration and has energy storage ability. Stainless steel and aluminum materials with different thicknesses use as thermal cell absorbers then aluminum materials use as a flat plate absorber base-collector. The experiment performs using a solar simulator with solar radiation of 700 W/m2. Referring to the results in term of heat storage (Qstorage), the heat transfer rate of the collector (Q ̇) and efficiency of the collector shows that stainless steel 1.0 mm with an aluminum base absorber (Case E) has a higher value which is 412 kJ, 18.21 kW, and 47.08 %, respectively. The higher total energy gain collected at the bottom plate as dummy load in the drying chamber (T1 and T2) is stainless steel 1.0 mm with an aluminum absorber base-collector (Case E) value of 2.85 kJ. Stainless steel 1.0 mm with an aluminum absorber base-collector (Case E) has the maximum value of energy gain at 300 seconds which is 116.08 J for the bottom plate (T1 and Ta). Flat plate base absorber thermal cell (FPBTCA CASE E) shows better performance in thermal storage than Flat Plate Solar Collector (FPSC).
Downloads