Thermal Characteristics of an Unsteady Hybrid Nano-Casson Fluid Passing Through a Stretching Thin-Film with Mass Transition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.104.2.3650Keywords:
Thin-film, Casson hybrid nanofluid, Keller Box method, homotopy analysis method, mass transition (injection)Abstract
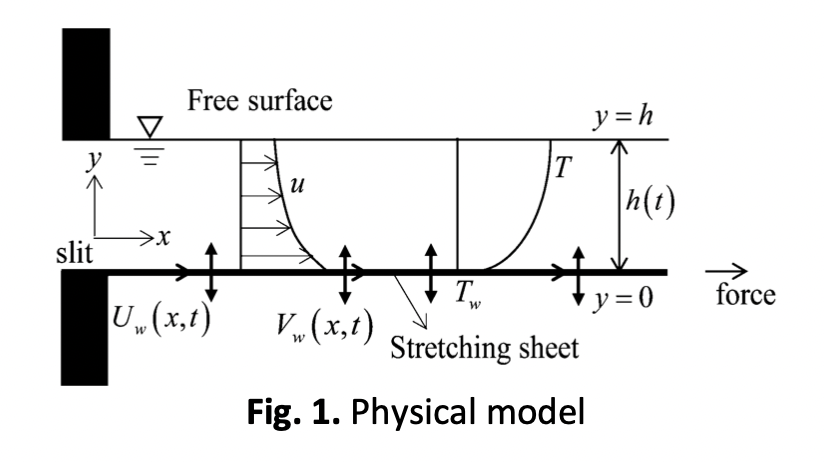
In current communication, the thin-film flow of Casson hybrid nanofluid consists of copper and alumina nanoparticles that dissolved in carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) plus water over an unsteady stretching porous sheet is elucidated. Using suitable similarity variables, the resultant partial governing equations are turned into a set of nonlinear ordinary differential equations. The Keller box approach is then used to solve the transformed equations. The unknown thin-film thickness constant is determined by using the homotopy analysis approach. The thermal and velocity distributions, as well as the Nusselt number and skin friction of the fluid, are discussed for different values of relevant parameters such as thin-film thickness, nanoparticles volume fraction, and mass transition parameter. The distributions of temperature and velocity decrease when the thin-film thickness is increased. The velocity distribution is decreased by the Casson, nanoparticles volume fraction, and mass transition (injection) parameter. The temperature is enhanced by the nanoparticle's volume fraction and the Casson parameter, however, has an opposite tendency with the mass transition (injection) parameter. For the physical quantities, the skin friction has a negative function with all the parameters. The mass transition (injection) parameter increases the Nusselt number. The outcomes of the present study are useful for example in producing the smart contact lens that has been used in the biomedical field.
Downloads