Hydrodynamics Analysis of Mixing Process in Fermenter
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.109.1.7190Keywords:
CFD, hydrodynamics, fermenter, mixingAbstract
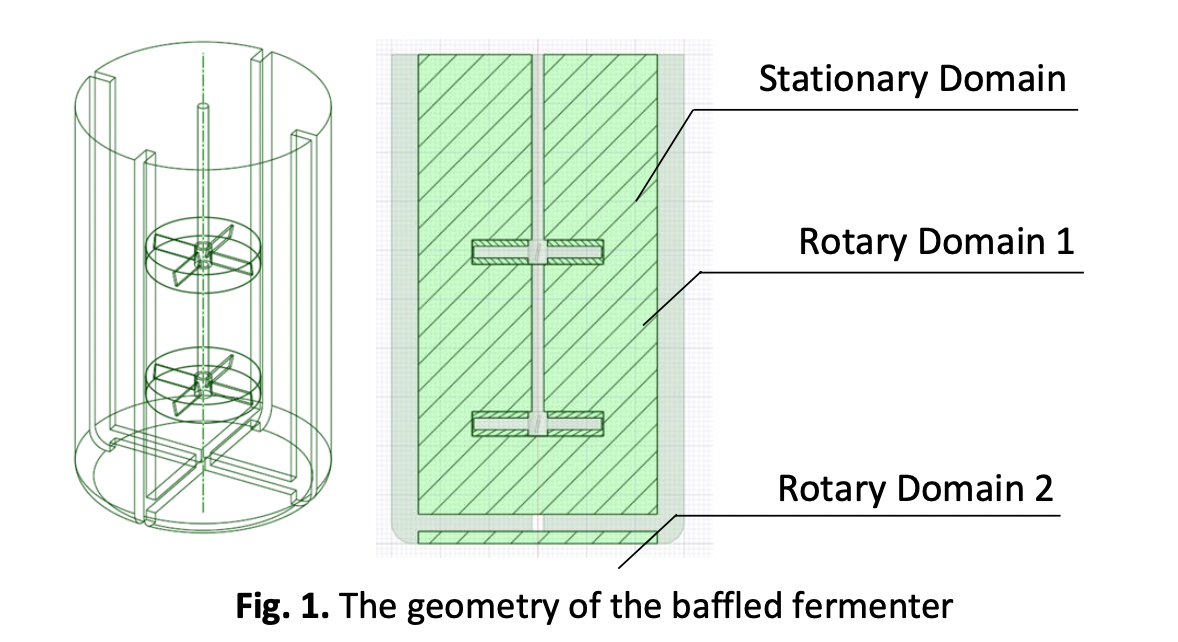
The perfect mixing process ensures the ideal substrate conditions for microorganisms to live to produce ethanol in the fermenter. The critical factors that affect the mixing process are the agitation speed, baffle configuration, and the impeller type. The Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software can make the study of fermenter hydrodynamics more convenient due to the cost savings of expensive apparatus and less time-consuming. This study aimed to examine the hydrodynamic characteristics of a fermenter using the ANSYS FLUENT 2021 R1 software and its validation. The hydrodynamics of the mixing process in the dual-pitched blade impeller bioethanol fermenter in agitation speeds of 200 to 1000 RPM and the effect of baffles were observed by simulation and experimentally. The realizable k-epsilon turbulence model and the Eulerian volume of fluid mixture multiphase model were used in this CFD simulation. The simulation results were relatively close to the experimental with similar flow patterns and low mixing time error, which is 7.9% on average. The results show that the higher the agitation speed, the higher the torque, power, and shear stress. The increasing agitation speed caused the lower mixing time. A faster mixing time was obtained in the fermenter with no baffle configuration.
Downloads