A Computational Technique for Low-Cycle Fatigue of LNG Mixing-Tee Weldment – An Industry Case Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.104.2.103114Keywords:
Computational analysis, mixing-tee, liquefied natural gas, fatigue life cycle, thermal stressAbstract
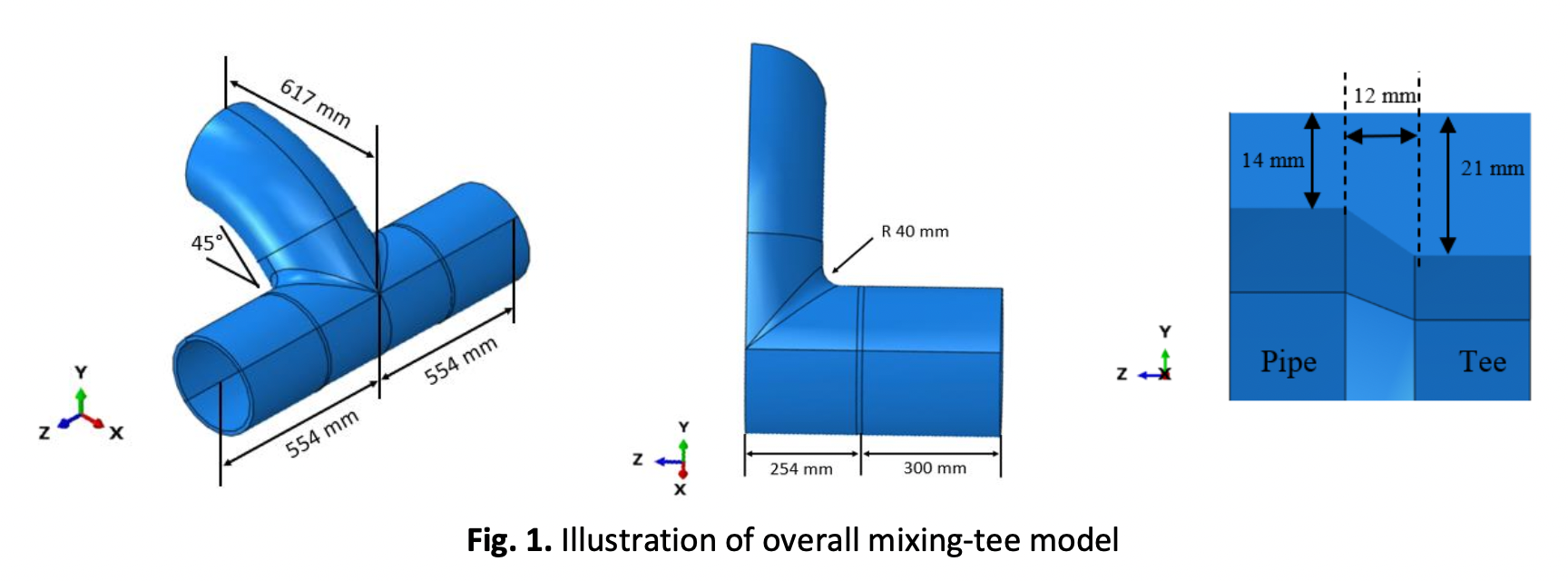
This research describes a computational method for low-cycle fatigue cracks in LNG mixing-tee weldments. Using a combination of thorough finite element modelling and fatigue life prediction with the finite element software ABAQUS and FE-Safe, the approach is able to simulate the thermal stresses and fatigue damage of a mixing-tee subjected to thermal cycle. The approach consists of three primary phases. First, the thermal distribution at the mixing-tee junction caused by the mixing temperature of the liquefied natural gas (LNG) is predicted. These first-step solutions are then included into second-step modelling, which simulates the thermal stress of the mixing-tee. The next phase entails modelling the fatigue behaviour of the mixing-tee using the thermal stress data. The computed fatigue life cycle achieves a 92.8% accuracy level when compared to real on-site observations. The suggested method enables the accurate prediction of thermal and fatigue behaviours within a tolerable computational time.
Downloads