Theoretical and Numerical Study on the Effect of Ambient Temperature towards Gas Dispersion in Indoor Environment using CFD Approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.105.1.194209Keywords:
Harmful gas dispersion, harmful gas behavior, thermofluidsAbstract
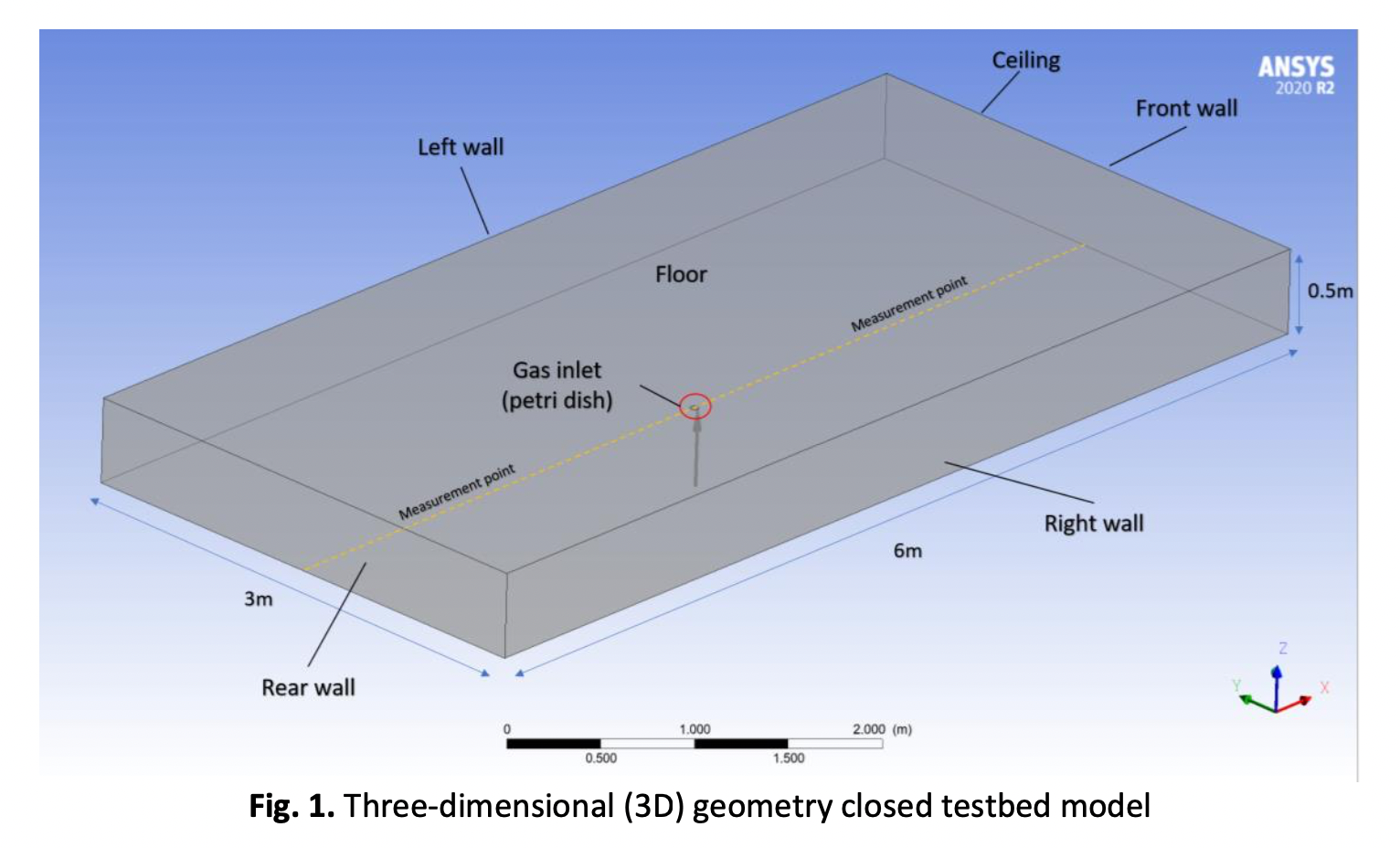
The usage of harmful chemical gas and natural gas has been increasing rapidly which increase the risk of gas leakage incident to occur especially in the indoor environment. It is important to learn the gas dispersal behavior in order to mitigate the casualty caused by gas leakage. In addition, one of the factors that contribute to the dispersion of gas is temperature. This paper focuses to study the role of ambient temperature toward gas dispersion in an indoor environment by looking at the theoretical and numerical knowledge of gas diffusion's relationship with temperature. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has been utilized to simulate gas dispersion at different ambient temperature levels in an indoor environment. This study released ethanol vapor to simulate gas dispersion at 5°C, 25°C, and 40°C of ambient temperature to observe the way gas distribute in the indoor environment. Both results from the theoretical calculation and simulation were compared. The result indicates that the gas diffusivity has an increment of 3.5% for every 5°C increment of the temperature. This causes the gas to diffuse rapidly in the warm air compared to the cool air. This paper also finds out that when the initial ambient temperature which is 5°C, was increased to 25°C and 40°C it causes the spread distance of the gas increased by 13.75% and 32.50% respectively.
Downloads