Computational Study on the Influence of Duct on the Performance of Darrieus Hydro-Turbine
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.105.1.210219Keywords:
Blade design, HAWT, CFD Fluent, power coefficient, torque coefficientAbstract
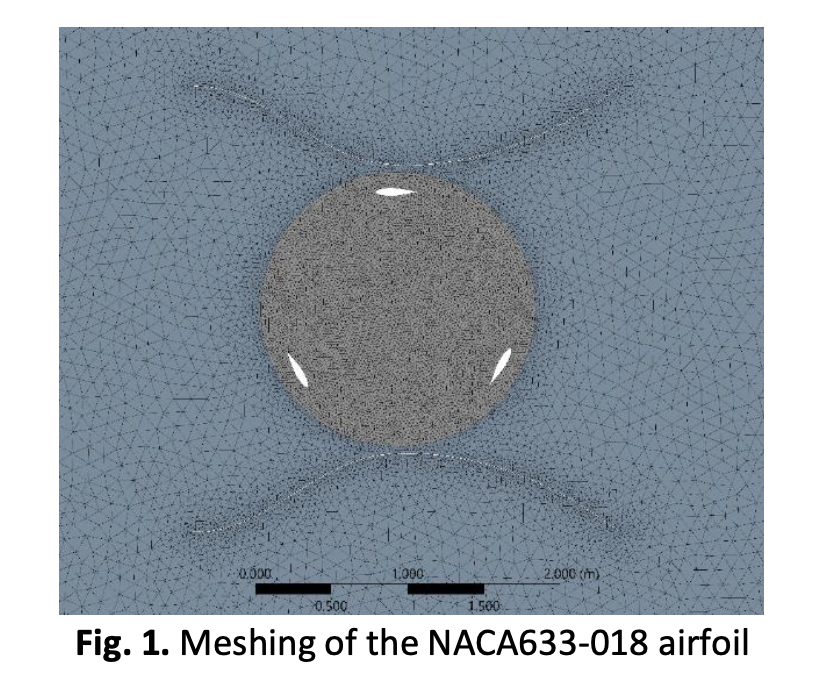
Hydropower is considered one of the most reliable, inexpensive and environmentally friendly sources of renewable energies and it is predicted to play a significant role in future sustainable energy systems. The straight-blade Darrieus turbine is receiving more attention as it is simple to build at an inexpensive cost. However, Darrieus turbines still have a lower efficiency as opposed to axial turbines. Therefore, in this study, the Darrieus turbine is equipped with a duct geometry in the center in order to enhance its conversion efficiency using the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation technique. A 2D simulation model with NACA 663-018 airfoil profile is developed to perform the simulation in Ansys Fluent software while using the K-ω shear stress transport (SST) as the turbulence model. The computational simulations cover a parametric study based on the variation of the rotational speeds while keeping the upstream velocity constant. The performances are evaluated in terms of power, power coefficient, torque and torque coefficient. The simulation results showed that the power coefficient and torque coefficient were found to increase with the rotational speeds with the highest efficiency at the TSR of 2 and then decrease. A similar conclusion was drawn in terms of power and torque output. However, the maximum power coefficient and torque coefficient were about 54% and 27%, respectively.
Downloads