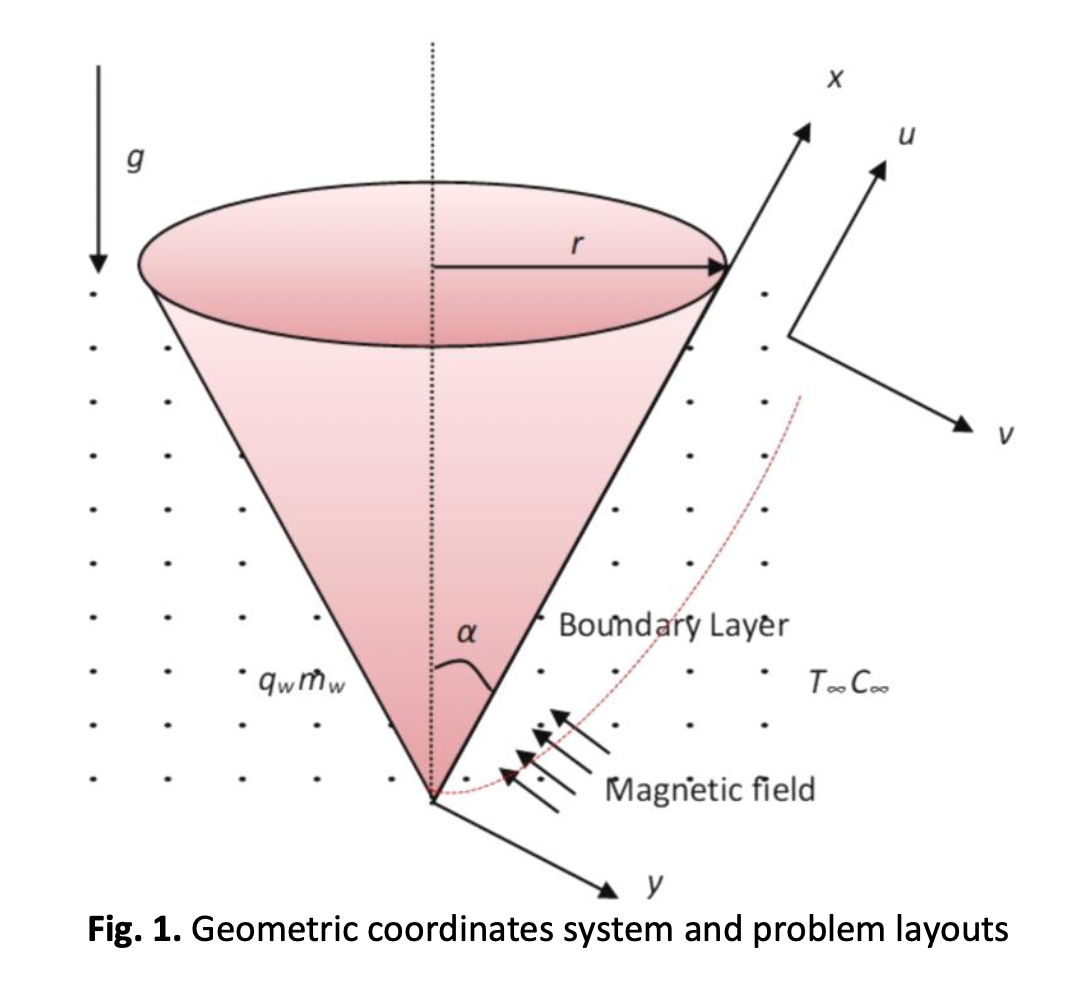
Unsteady Free Convection Dusty MHD Flow with Dissipation Effect Over Non-Isothermal Vertical Cone
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.114.1.5668Keywords:
Dusty fluid, magnetohydrodynamic, Crank-Nicolson method, coneAbstract
The implications of suspended particles on MHD flow in a viscous fluid over a non-isothermal vertical cone with dissipation effect was investigated in this recent research. To maximise process efficiency and avoid equipment failure, it is important to thoroughly investigate the complex and dynamic behaviours that might result from the interaction between the fluid and the dust particles inside the cone. The Crank-Nicolson method will be used in the study to analyse the mathematical model quantitatively. MATLAB software was used to compute the discretization equations and depict the numerical outcomes. The velocity distribution, temperature distribution, skin friction and Nusselt number affected by Prandtl number, magnetic, mass concentration of particle phase, viscous dissipation and fluid-particle interaction for particle and fluid phases are presented graphically as well as in a table and are thoroughly analysed. The outcome indicated that the fluid and dust phase velocity decreases when magnetic, mass concentration of particle phase and fluid-particle interaction parameters are escalated while viscous dissipation parameter shows an opposite behaviour. Moreover, the temperature and velocity profiles for the fluid phase are consistently greater than those for the dust phase in every result that was examined.
Downloads