Phase Behavior and Phase Equilibria for The Polydisperse Polyethylene + Ethylene + Hexane System at High Pressures and Temperature: Experiments and Correlations
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.112.2.4353Keywords:
Phase behavior, phase equilibria, polydisperse polyethylene, Sanchez-Lacombe EoS, solution polymerizationAbstract
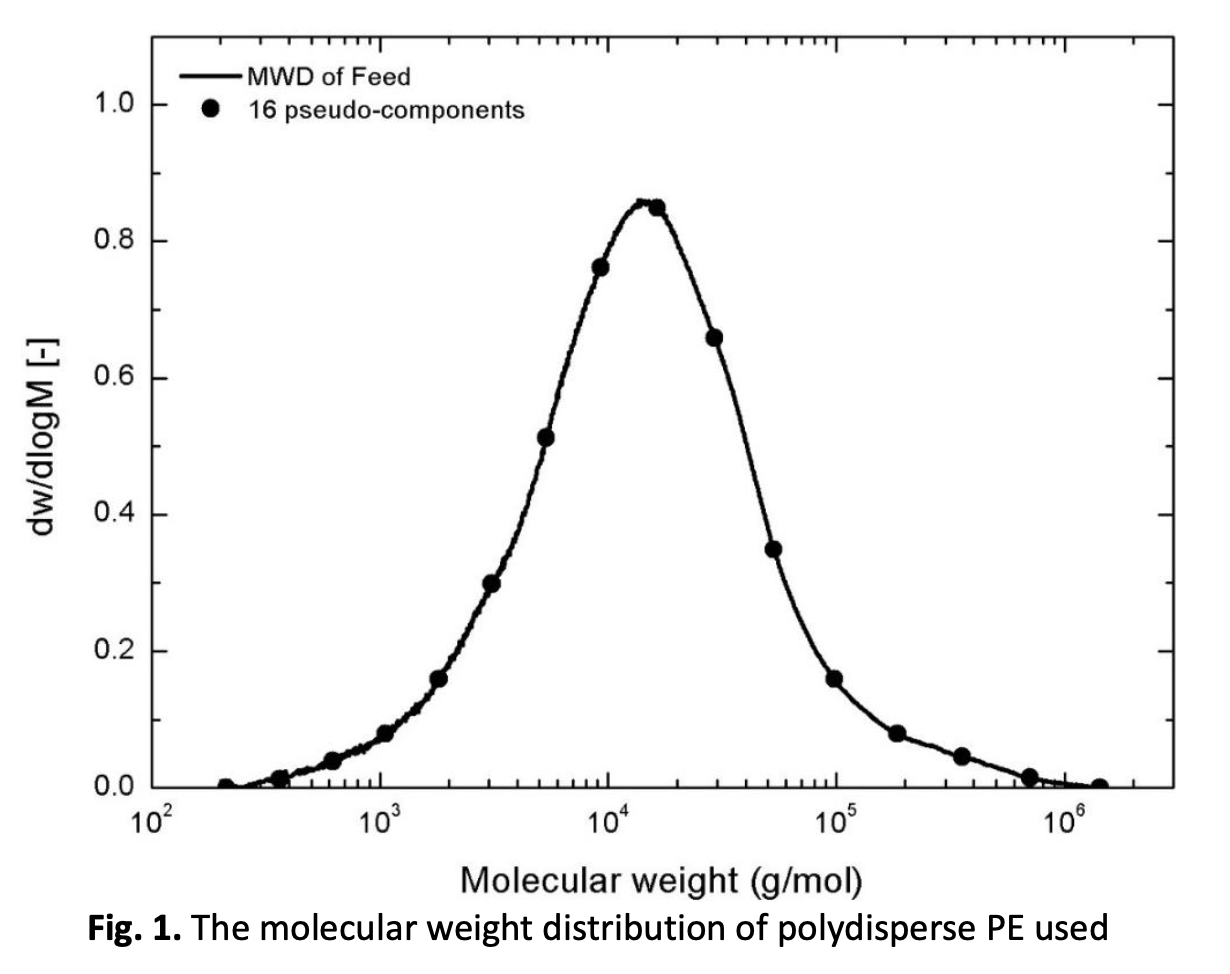
This study aims to provide experimental phase equilibrium and phase behavior data for polydisperse PE + ethylene + hexane system. Polydisperse PE (Mw 30.0 kg/mol, PDI 4.2) was used with feed PE weight fraction, ⱳF,PE, of 0.02 to 0.20. The experiments based on a synthetic method were conducted at 473.2 K using an apparatus consisted of an equilibrium cell equipped with sampling tubes for solvent-rich and polymer-rich phases. The LL phase separation pressure increased by about 1 MPa for 1 wt% increase in ethylene concentration. The weight fraction of PE in solvent-rich phase, ⱳS,PE, decreased as the ⱳF,PE and pressure decreased. Similarly, the weight fraction of PE in polymer-rich phase, ⱳP,PE, also decreased as the ⱳF,PE decreased. The solvent-rich phase contained lower molecular weight fractions of PE, while the polymer-rich phase contained higher molecular weight fractions. These results were correlated and predicted with the Sanchez-Lacombe (S-L) EoS. Finally, the effects of pressure and ⱳF,PEon solvent recovery ratio were investigated with the S-L EoS. The results provided in this study could be used to obtain the higher hexane recovery by controlling the LL separation pressure.
Downloads