Investigating the Effects of Wu's Slip and Smoluchowski's Slip on Hybrid TiO2/Ag Nanofluid Performance
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.107.2.236252Keywords:
Wu’s slip, temperature jump, hybrid nanofluidAbstract
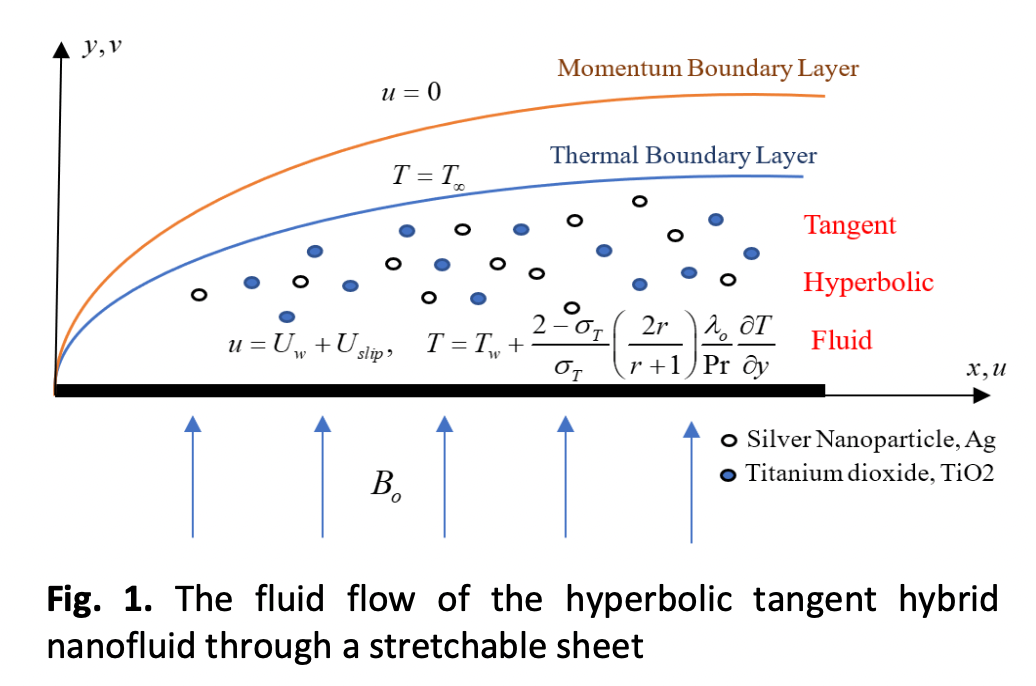
The high thermal conductivity of Titanium dioxide (TiO2) makes it ideal for heat transfer, particularly in a solar collector. However, nanofluids containing dissolved TiO2 nanoparticles tend to agglomerate. Thus, nanoparticle silver (Ag) is used to stabilize the nanofluid. This study looks at a hybrid nanoparticle of TiO2 and Ag, which are put into water to make a hybrid nanofluid, over a stretching plate. The effects of Wu’s velocity slip and Smoluchowski’s temperature slip are taken into consideration. Xue's thermal conductivity model for the hybrid nanofluid is employed. The governing equations are transformed by applying the similarity transformation technique and solved semi-analytically using the Homotopy Analysis Method. The effect of the multiple slips on the fluid profiles is graphically displayed and discussed. Results illustrate that the temperature profile is diminished by 42% due to Smoluchowski's temperature slip parameter, while the velocity profile is reduced by more than 40% due to the first and second-order Wu's slip parameters. These findings are important for optimizing the performance of the hybrid nanofluids. For example, in the solar collector, where a better understanding of heat transfer fluid characteristics can improve the stability of the hybrid nanofluid and the efficiency of eco-friendly energy storage.
Downloads