Effects of Tributyl Citrate Plasticizer on Thermomechanical Attributes of Poly Lactic Acid
Keywords:
PLA, TBC, plasticizer, thermomechanical traits, storage modulusAbstract
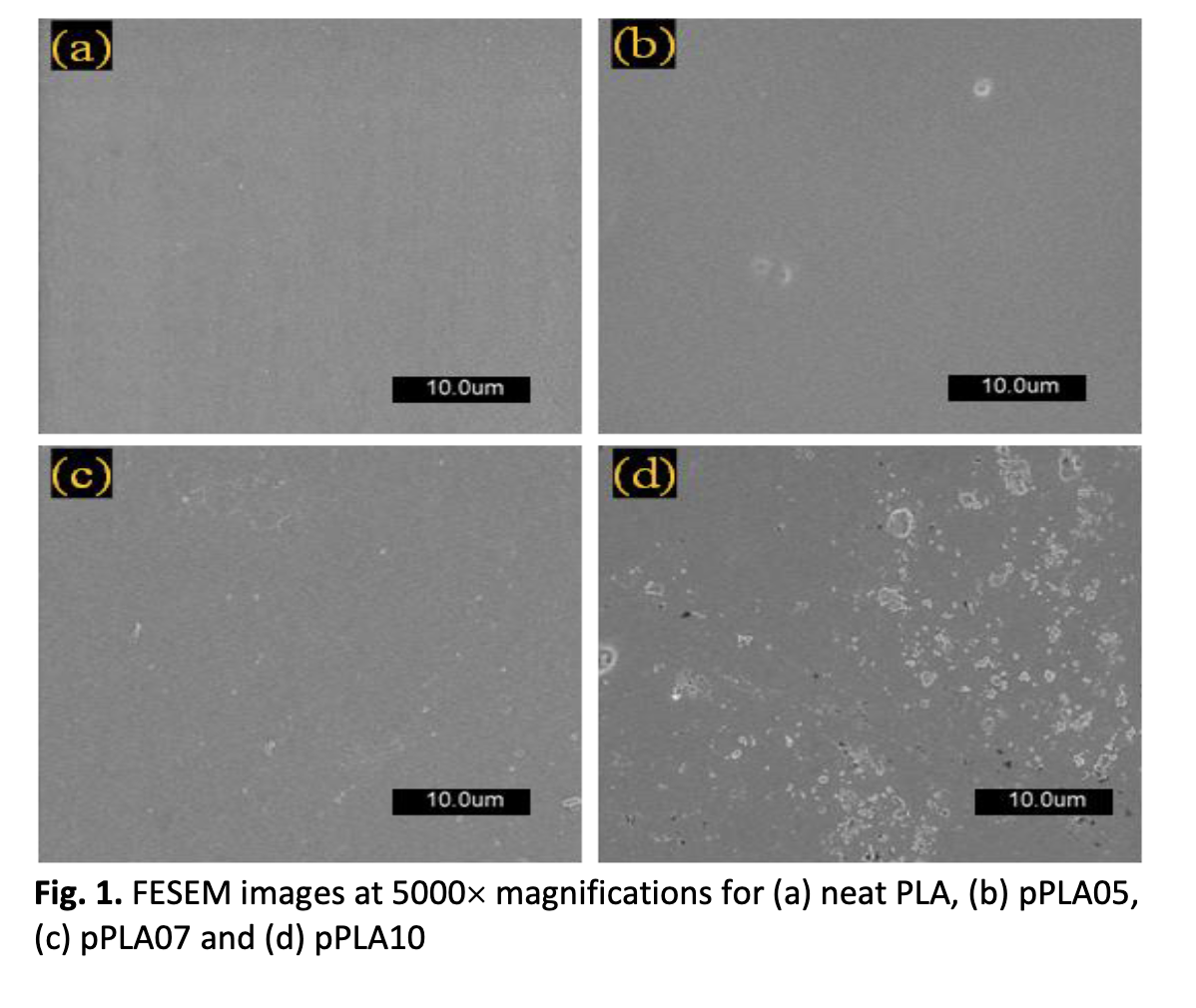
Unique physicochemical and barrier attributes of a biodegradable and sustainable polymer called poly (lactic acid) (PLA) is promising for various applications. Conversely, the issues related to the rigidity and fragility of this polymer that limits its wide usage needs to be inhibited. To surmount these shortcomings, various plasticizers have been incorporated into PLA to soften and make it useful for food packaging. In this research, tributyl citrate (TBC) was inserted as plasticizer into PLA matrix to modify its properties. The impact of varying TBC contents on the morphology, thermal and dynamic mechanicalbehaviourof PLA/TBC composites were evaluated. FESEM images of PLA composites revealed homogeneous fractured surfaces. The crystallinity of PLA/TBC composites was increased with the addition of plasticizer without altering its transparency. The values of the storage modulus and glass transition temperatures, the cold crystallization temperatures as well as the melting temperatures were discerned to be lowered. Furthermore, the dynamic mechanical analysis disclosed a drop in the storage modulus of 2.11GPa at 7wt·% of TBC inclusion, indicating enhanced flexibility of TBC modified PLA. It was asserted that the inflexibility and brittleness associated with pristine PLA can considerably be improved by activating it with the additive plasticizer TBC.
Downloads