Velocity Distribution and Base Pressure Analysis of under Expanded Nozzle Flow at Mach 1.0
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.92.1.177189Keywords:
Annular rib, Velocity distribution, Base Pressure, Expanded NozzleAbstract
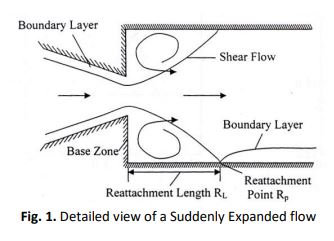
This paper discusses velocity distribution and base pressure control using annular ribs. The annular ribs are located in the enlarged duct. Its impact on the velocity distribution and base pressure changes from a converging nozzle at the sonic Mach number is investigated numerically using ANSYS software. The rib’s height is fixed to 3 mm while the rib’s height is varied from 1 mm to 2 mm. The simulation is performed by placing the rib at various locations in the duct namely 1D, 2D, 3D and 4D and at Nozzle Pressure Ration (NPR) varied from 1.5 to 5. The changes in base pressure (Pb) and velocity variation inside the duct are studied. The presence of rib in the duct causes disturbance in the flow field hence increases the Pb. The tendency of Pb to increase is observed as the height of the rib increases. Varying the NPR from 1.5 to 3 reduced Pb due to shock wave formation. The NPR increases with Pb as the flow undergoes under-expansion due to the expansion fan at the nozzle exit. The changes in Pb are consistent with velocity distribution inside the duct. The increase in turbulent kinetic energy is more significant due to the presence of rib, as compared to duct without rib. For lower NPR, the velocity is found to be highest at the axial direction of the duct while the highest velocity is found just ahead of the nozzle exit at higher NPR.
Downloads