Effect of Expansion Level and Relief to Shear Layer in a Suddenly Expanded Flow: A CFD Approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.100.3.202229Keywords:
Flow control, supersonic flow, NPR, base pressure, CD nozzleAbstract
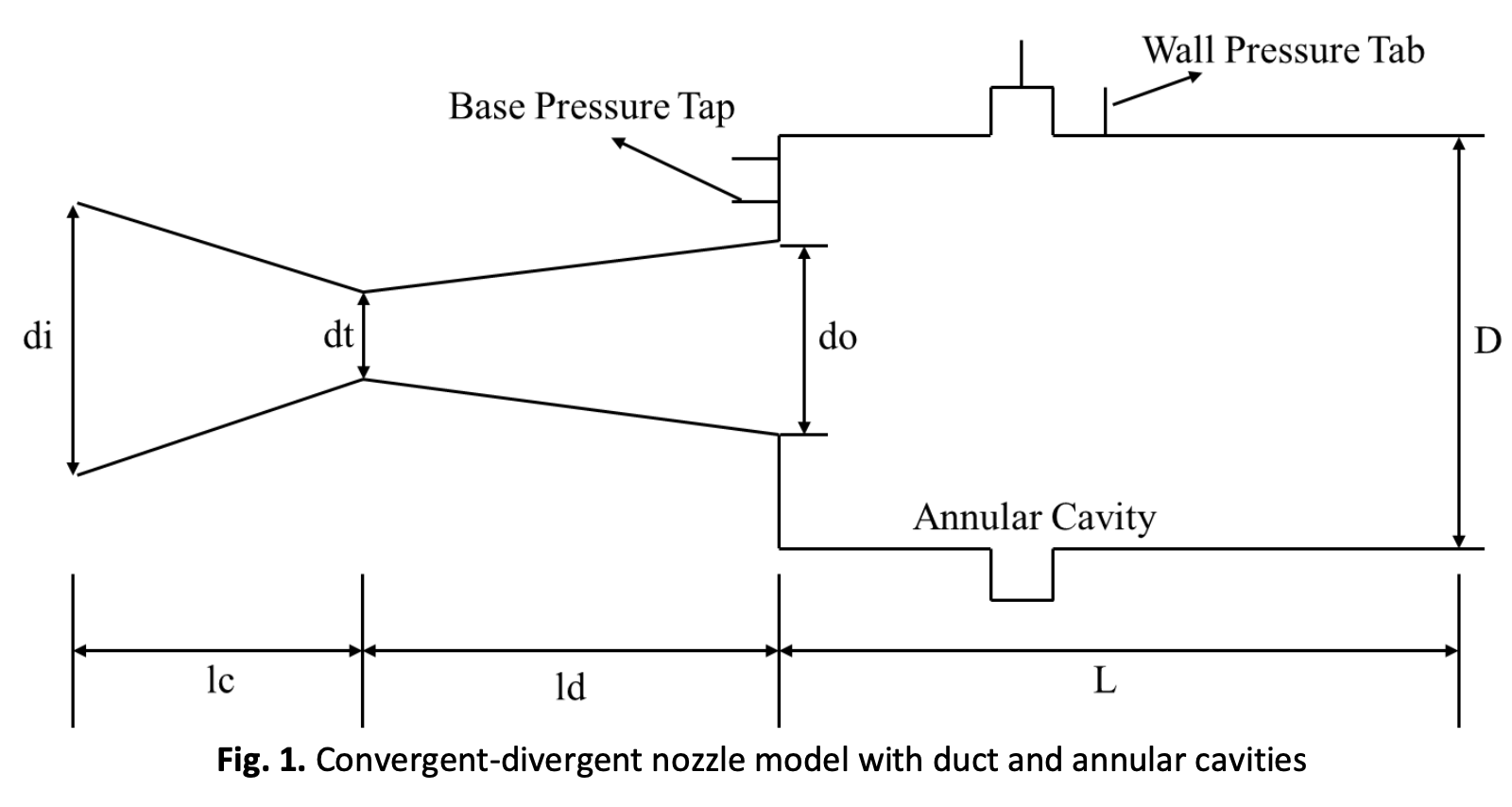
Computational Fluid Dynamics analysis was used to study the effect of expansion level in a suddenly expanded flow for a converging-diverging nozzle expanded to the duct of larger diameter at supersonic Mach number. Parameters include the nozzle pressure ratio (NPR), L/D ratio, and area ratio. The model of the converging-diverging (C-D) nozzle suddenly expanding into the enlarged duct with the cavity was created using the Design Modeler of ANSYS Fluent. The Mach number of the study is 1.6. The area ratio varied from 2.25 to 5.29, and the L/D ranged from 1 to 10. The simulated nozzle pressure ratio (NPR) ranged from 2, 3, 4.25, and 6.375. The outcome demonstrated that the geometric alteration and NPR strongly affect the base pressure. The ambient pressure influences result in lower L/Ds. The cavity of aspect ratio 1 is most effective in raising the base pressure. Increasing the width does not yield any desirable results. However, the location of the cavity played a very significant role in base pressure regulation. The duct's wall pressure and the flow field remained identical with and without control.
Downloads