Performance Testing and Analysis of Gravitational Water Vortex Turbine: A Modified Experimental Study on Blade Arc and Inclination Angle
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.109.1.147161Keywords:
Blade arc angle, blade inclination, Gravitational Water Vortex Turbine (GWVT)Abstract
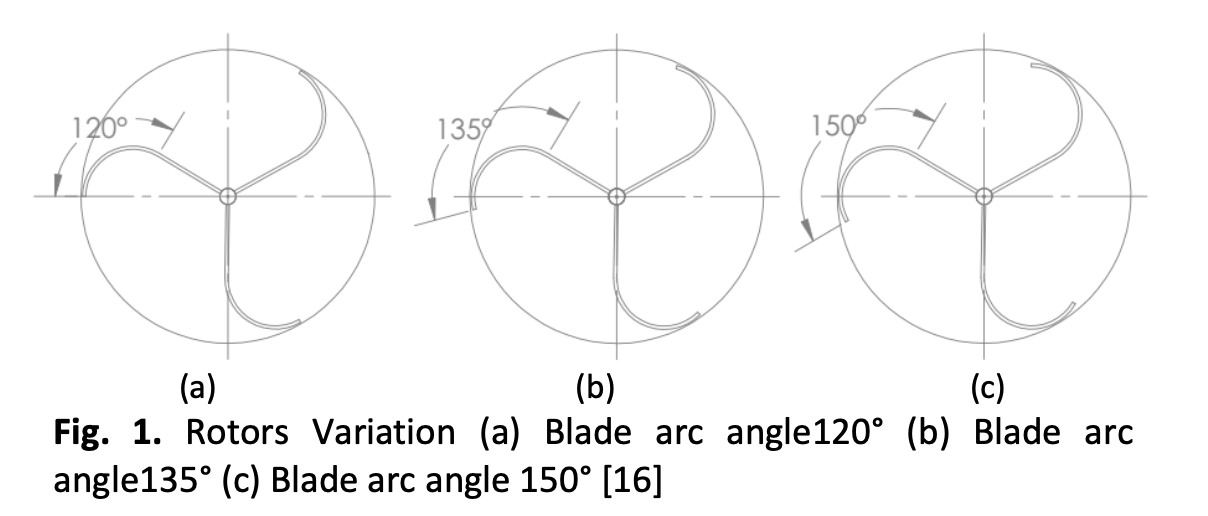
Dams’ systems were constructed to create higher water levels as high as head for generating renewable power. However, the construction process has impacted environmental changes such as land dredging and displacement of population settlements. Therefore, using a micro hydro power plant is the one of the solutions because this power plant is environmentally friendly and could help to facilitate the balance of the environmental ecosystem. This study aims to investigate the performance of a Gravitational Water Vortex Turbine (GWVT) with the blade arc and inclination angles. A Gravitational Water Vortex Turbine (GWVT) is a form of micro hydro turbine that does not require a large dam for its use, as well as a simple design model that can reduce maintenance and installation costs. This study conducted a laboratory-scale experimental study on GWVT turbines using a low-speed water canal and considered the varied shape and angle of inclination of the turbine blade profile. A conical basin and three different discharge variations were considered in this study. The discharge variations are 7.5×10-3 m3/s, 8.5×10-3 m3/s, and 9.5×10-3 m3/s. This study designed and tested a prototype L-type runner with three inclination angles: 60°, 70°, and 80°. Based on the data, the runner with 60° blade inclination with 90° blade arc angle produced the highest turbine efficiency, followed by 75° and 105° blade arc angles.
Downloads