A Review on Hydrogen Separation through Inorganic Membranes
Keywords:
Inorganic membrane, hydrogen separation, palladium deposition, gas permeationAbstract
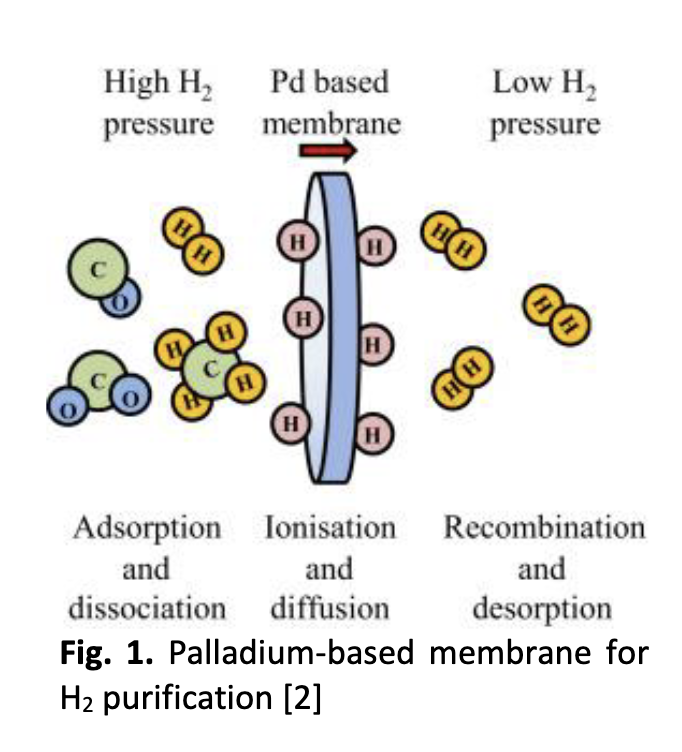
The process of membrane separation is indicated as attractive choices than mature technologies for example cryogenic distillation as well as pressure swing adsorption. Hydrogen (H2) of high purity can be acquired via membranes of dense metallic and mainly palladium as well as its alloys with highly selective properties to H2. Composite membranes improvement via deposition of thin metallic layer on inorganic or porous polymeric supports is deemed as an effective technique in improving gas permeation of dense metallic membranes. Membranes of inorganic materials demonstrated excellent separation performance in purifying H2. In addition, these membranes are appropriate for high temperature separation application, which is preferable through high-temperature WGS reaction as well as pre-combustion CO2 capture.This paper presented mini review on hydrogen separation via inorganic membranes, taken into account both porous and nonporous type membraneto make known of recent investigation and for further optimization.
Downloads