Feasibility Study of Plasma Actuator for Flow Separation Control
Keywords:
Plasma actuator, active control, flow separation controlAbstract
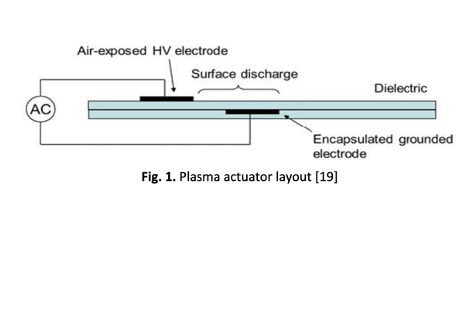
The plasma actuator, or dielectric barrier discharged (DBD) actuator, is a flow control technique which comprises three simple components, namely, an exposed electrode, a dielectric layer, and a covered electrode. By providing sufficient applied voltage, the air will locally ionize. In the presence of the electric field, the ionized air induces thrust in the surrounding air, thus jetting the flow in the stream-wise direction, and momentum will be generated in the ambient air, which forms the basis for flow separation control strategy. This project presents the findings of experimental testsand numerical simulations on the operation of plasma actuator under several input conditions and geometries in order to investigate the feasibility of plasma actuator to control the flow separation. An experiment was conducted to visualize the formation of plasma on 0.15 mm thick of Kapton dielectric actuator under an applied voltage of5 to 10 kVp-p. The results demonstrate that, by increasing the input voltage, the generation of plasma also increases. Moreover, numerical analysis of plasma actuator under various applied voltages, dielectric materials, dielectric thicknesses,and covered electrode widths were computed using COMSOL Multiphysics software. Based on the findings, the trend of the results produced is nearly similar to those of previous researchers. However, further studies are needed toinvestigate the impact of gas temperature, pressure and flow velocity on the discharge of a plasma actuator.
Downloads