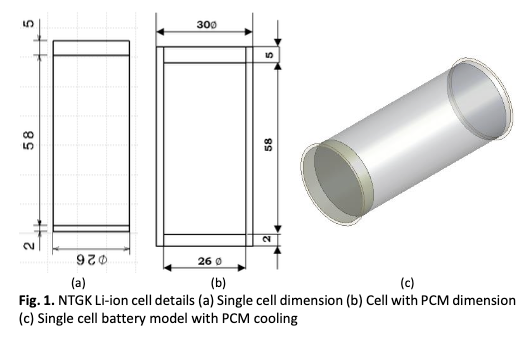
Enhancing Battery Thermal Management in Li-ion-Powered Electric Vehicles using Phase Change Material-based Systems: A Multi-Scale CFD Simulation Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.110.2.6678Keywords:
Li-ion battery, PCM, Battery Thermal ManagementAbstract
Electric cars (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are propelled by Li-ion batteries for a clean and sustainable future. Under harsh and abusive conditions, a battery pack generates a lot of heat, which could result in a disastrous thermal runaway. The current work suggests a Battery Thermal Management System (BTMS) based on Phase Change Material (PCM) to prevent thermal runaway. Using ANSYS's multi-scale, multi-dimensional Newman, Tiedemann, Gu, and Kim (NTGK) model, a 3D simulation of a single battery with PCM, is carried out. The thermal performance and discharge behavior of the battery pack is analyzed by the NTGK model. The solidification and melting model is combined with the NTGK for PCM-based BTMS. Under harsh and abusive circumstances, the effect of different discharge rates on the thermal performance of 26650 Li-ion cell with and without PCM is investigated. The PCM-based BTMS reduces the maximum battery temperature by 2.243 K ,1.44 K, and 2.5 K and increases temperature uniformity at 0.5C ,1C and 1.5C discharge rates, respectively. The data available from this research will be useful in the development of passive BTMS for EV applications.
Downloads