The Effect on The Volume and Semi Axes of a Conducting Spheroid Due to The Scaling on Its First Order Polarization Tensor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.94.1.118Keywords:
Matrices, Polarization of Pólya-Szegö, Depolarization Factors, Virtual Mass, Integral EquationsAbstract
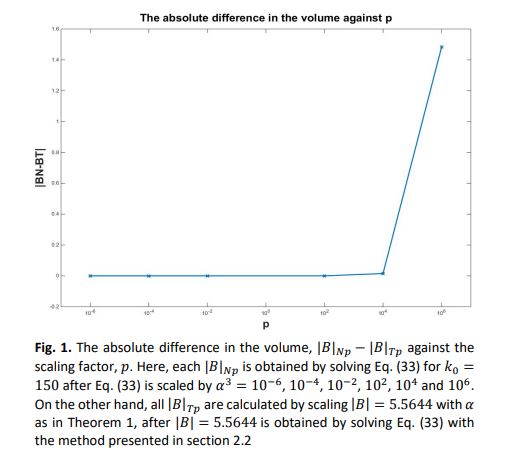
In order to enhance identification of objects in electrical imaging or metal detection, the polarization tensor is used to characterize the perturbation in electric or electromagnetic field due to the presence of the conducting objects. This is similar as describing the uniform fluid flow that is disturbed after a solid is immersed in the fluid during the study of fluid mechanics. Moreover, in some applications, it is beneficial to determine a spheroid based on the first order polarization tensor in order to understand what is actually represented by the tensor. The spheroid could share similar physical properties with the actual object represented by the polarization tensor. The purpose of this paper is to present how scaling on the matrix for the first order polarization tensor will affect the original spheroid represented by that first order polarization tensor. In the beginning, we revise the mathematical property regarding how scaling the semi axes of a conducting spheroid has an effect to its first order polarization tensor. After that, we give theoretical results with proofs on how scaling the matrix for the first order polarization tensor affects the volume and semi axes of the spheroid. Following that, some numerical examples are provided to further justify the theory. Here, different scalar factors will be used on the given first order polarization tensor before the new volume and semi axes of the spheroid are computed. In addition, we also investigate how the size of the scale on the first order polarization tensor influence the accuracy of computing the related volume and semi axes. In this case, it is found that a large error could occur to the volume and the semi axes when finding them by solving the first order PT with that has being scaled by a very large scaling factor or a too small scaling factor. A suggestion is then given on how to reduce the errors.
Downloads