The Influence of Window-to-Wall Ratio (WWR) on Airflow Profile for Improved Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) in a Naturally-Ventilated Workshop in a Hot-Humid Climate
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.116.1.139157Keywords:
Ventilation, airflow pattern, air velocity, workshop, Indoor Air Quality (IAQ), CFDAbstract
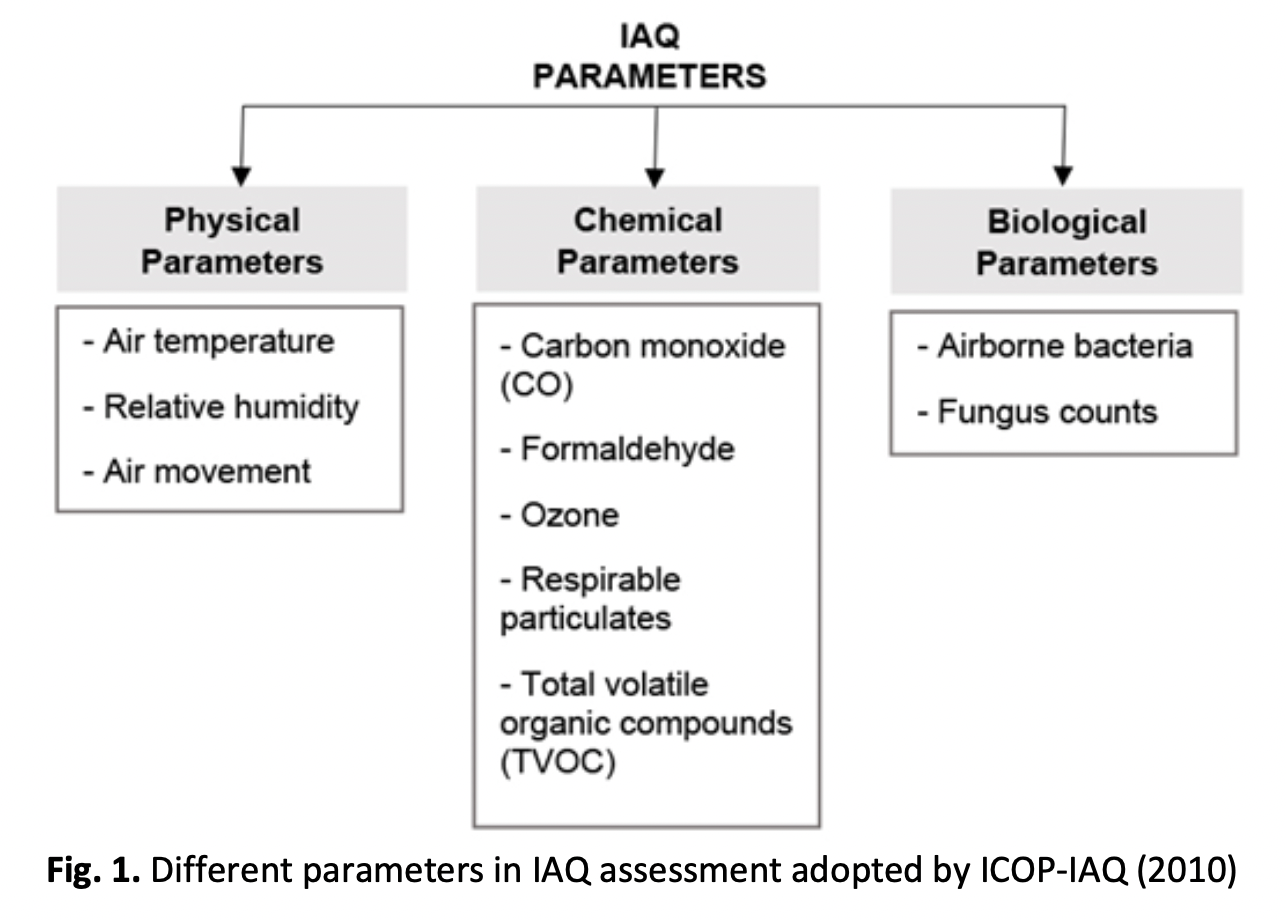
Indoor air quality (IAQ) has become a major concern worldwide as indoor air pollution rapidly becomes a public health issue. IAQ plays a pivotal role in occupants' health and comfort and influences their productivity and work efficiency. Many studies have been done on IAQ of common building spaces such as offices, residential buildings, and educational institutions, but the availability of IAQ studies on workshops is limited, considering the significant implications for workers' health and performance. Thus, this paper aims to study the effectiveness of natural ventilation in a workshop based on the influence of different window-to-wall ratios (WWR). Electronic databases are utilized to obtain data, and the findings collected are categorized based on research methodology, issues, and findings. The air movement as part of the physical parameters of IAQ is studied through the application of Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) simulation to observe and analyse the airflow pattern and the air velocity of the naturally ventilated workshop with different WWRs. The research outcome underscores the ideal WWR for effective natural ventilation in a workshop is 0.30. However, the study observes that the effectiveness decreases as WWR exceeds 0.50. Further research on the openings' location, inlet, and outlet sizes and application of mechanical ventilation can be conducted to improve the measurement of the IAQ effectiveness in a naturally ventilated workshop.
Downloads