Performance Analysis of Photovoltaic and Wind Turbine Grid-Connected Systems under LVRT Conditions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.115.1.143155Keywords:
Photovoltaic system, doubly-fed induction generator, low voltage ride-through, grid integration, reactive current injection, renewable energyAbstract
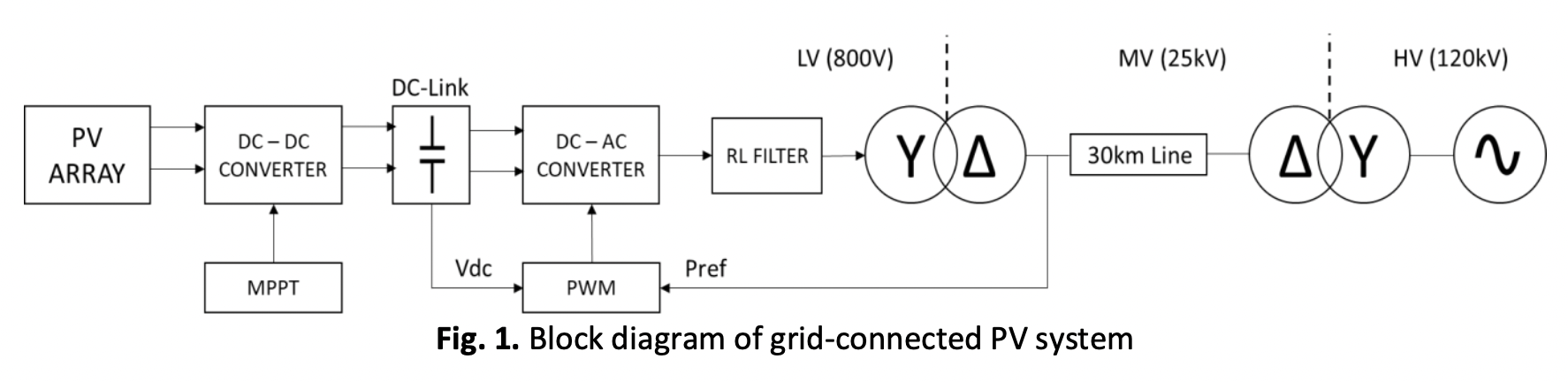
The integration of grid-connected renewable energy systems has gained significant attention and introduces several challenges and considerations. One of these challenges is ensuring the reliable and stable operation of these systems under various grid conditions. For example, faults at the grid could lead problems such as DC-link over-voltage and AC over-current that may cause disconnection or damage to inverter. This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the performance of photovoltaic (PV) and doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) wind turbine grid-connected systems under low voltage ride-through (LVRT) conditions. The study aims to investigate their behavior, and stability during LVRT events and provide insights for enhancing their grid integration capabilities. The PV and DFIG systems are modelled and simulated using MATLAB Simulink under three difference conditions, with and without using reactive current injection and DC chopper circuit. Various performance parameters, including grid voltage, grid current, DC-link voltage, active power, and reactive power, are analyzed to assess the system's behavior and compare their responses. The principal results reveal distinct performance characteristics of the PV and DFIG systems. The PV system shows higher overshoot currents, over-voltage, and significant drops in active power during fault occurrences, while the DFIG system exhibits lower overshoot currents and better stability in the DC-link voltage. Reactive power responses differ between the systems, with the PV system demonstrating a higher capability for support. The implementation of DC chopper shows more effective in the reduction of DC-link voltage and overshoot grid current in the PV system compared to the DFIG system.
Downloads