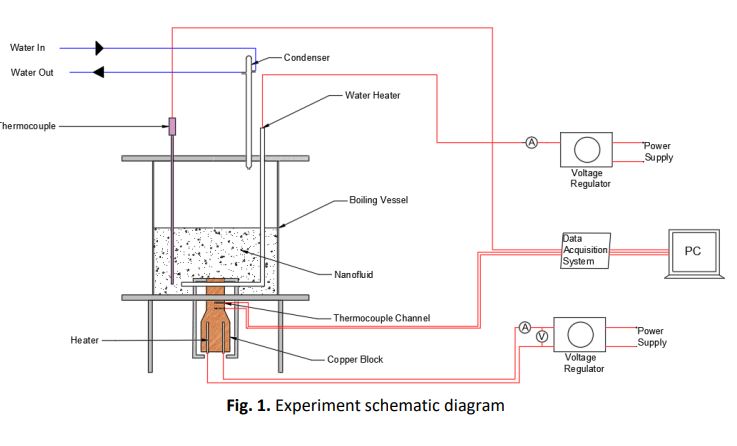
Boiling Heat Transfer Coefficient of Hybrid Nanofluids with and without Surfactant
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/armne.27.1.3141Keywords:
Aluminium oxide, silicon dioxide, titanium oxide, sodium dodecyl sulphate, metal oxide hybrid nanofluids, surfactant, boiling heat transfer coefficientAbstract
Experiments were carried out to investigate the effect of surfactants on the boiling heat transfer coefficient of hybrid water-based nanofluids. In the present work, both Al2O3-SiO2 and Al2O3-TiO2 hybrid nanofluids were prepared with a 75:25 composition ratio and concentration of 0.01 v/v%, mixed with SDS surfactant of 40 ppm and prepared using ultrasonic process. It was found that Al2O3-SiO2 and Al2O3-TiO2 hybrid nanofluid enhance BHTC performance compared with distilled water, however, its performance will deteriorate gradually after 5 minutes of the experiment. Additional SDS in both Al2O3-SiO2-SDS/Water and Al2O3-TiO2-SDS/Water hybrid nanofluid will increase its BHTC performances up to 112.27% and 127.03% respectively compared with distilled water. Al2O3-SDS has better BHTC performance compared with Al2O3-SiO2 and Al2O3-TiO2 hybrid nanofluid which is 327.15% compared with distilled water.
Downloads