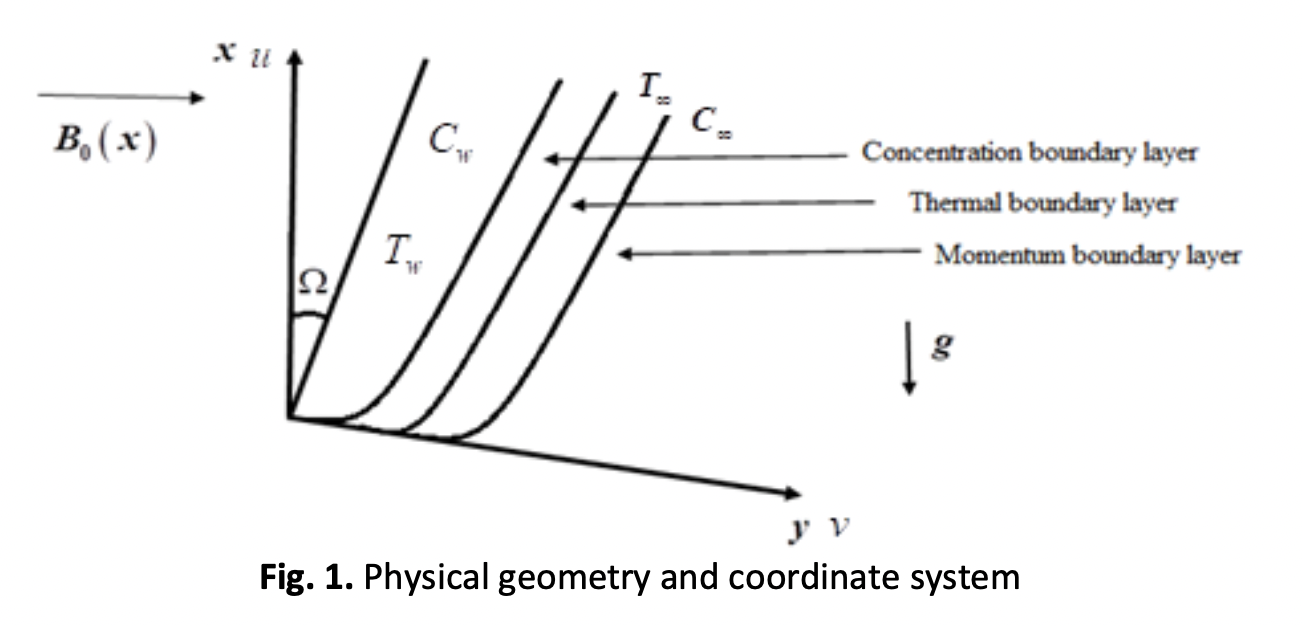
Impact on Casson Nanofluid Flow Across an Inclined, Slanted Surface by Radiation, Energy and Mass Transfer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.108.1.184202Keywords:
Casson nanofluid, thermal radiation, heat source, chemical reaction, NDSolveAbstract
Casson nanofluid flow across a porous, slanted surface is investigated. In addition to the impact of a heat source, thermal energy, and a chemical reaction also are considered. Applying similarity transformations, the controlling nonlinear PDEs are converted to ODEs. To resolve the ordinary differential equations (ODEs), we used the universal numerical differential equation solver Wolfram Language function NDSolve. The distributions under heat source are affected by chemical processes and other variables are explored. While liquid velocity reduced due to inclination and the Casson factor, mass and energy transit rates rose. The findings are represented graphically and are consistent with past research. The findings would provide valuable insights into the flow patterns, temperature distribution, and concentration profiles within the system. This information can be crucial for designing and optimizing heat transfer systems, energy-efficient processes, and catalytic reactors involving Casson nanofluids and porous media.
Downloads