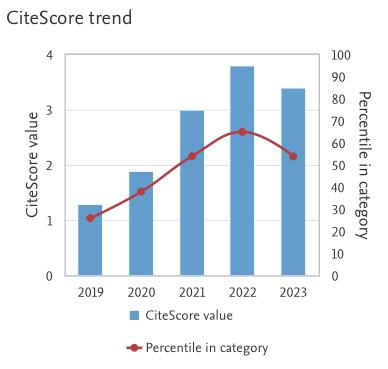
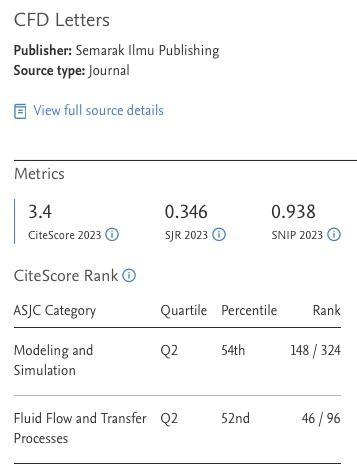
Study on the Addition of Nanoparticles in the Lead-free Solder During Reflow Soldering via Numerical Simulation - A Review
Keywords:
Lead-free solder, nanoparticle, reflow soldering process, numerical simulationAbstract
Surface mount technology (SMT) is a method of electronic components mounting or placed directly on the surface of the circuit board. The solder will be printed onto the substrate on the printed circuit board (PCB) and then undergoes reflow soldering process. As the used of lead (Pb) is restricted by the restriction of hazardous substances (RoHS) directive in 2006 and Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEE), the study on the addition of nanoparticles into the lead-free solder has increased as to increase the reliability and quality of the lead-free solder. Researchers have added Cobalt, Silver, Molybdenum, Diamond, Silicon, Zinc, Zinc oxide and many more to increase few solder criteria such as the wetting properties, mechanical properties and the intermetallic compound (IMC) layers. Many numerical simulation methods such as finite element (FEM), finite volume (FVM), Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM), discrete phase method (DPM), and molecular dynamic (MD) simulation have been used to clearly show the reflow soldering process and to cut the cost of experimental work.