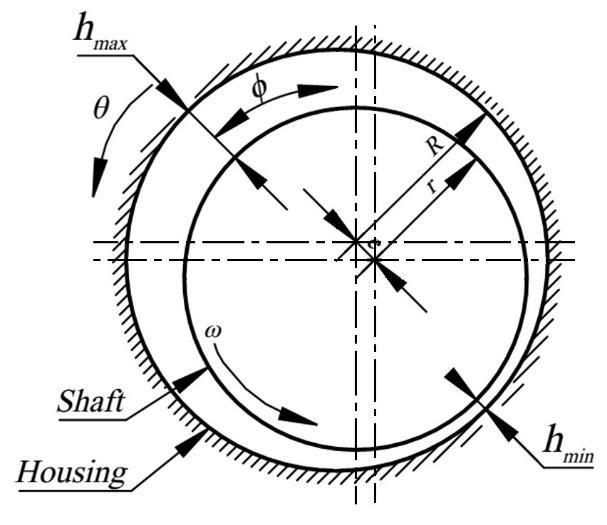
A Comparative Study on Hydrodynamic Analysis with and without Cavitation Modelling: A Study on Textured Slip Journal Bearing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/cfdl.16.8.4863Keywords:
journal bearing, lubrication, cavitationAbstract
In journal bearing modeling, the phenomenon of cavitation is very important to improve the accuracy of the simulation results. This is because cavitation will almost certainly occur because there are convergent and divergent geometries. The results of the simulation will be close to real conditions so that it can have a positive effect on researchers in order to design optimal journal bearings. The effect of modeling without cavitation and with cavitation on journal bearing modeling has a great influence on the lubrication performance of journal bearings. In modeling with cavitation, the maximum hydrodynamic pressure and load carrying capacity that the journal bearing is capable of relying on has a fairly rapid increase. The modeling results also relate to the friction force that occurs in the journal bearing. The aim of the present study is to explore the effect of inclusion of modeling of the Hydrodynamic pressure. The finite volume method based on software is used to compare the result with and without cavitation. Here, The mixture multiphase cavitation is adopted. The numerical result show t he effect of modelling without cavitation and with cavitation on journal bearing modelling has a great influence on the lubrication performance of journal bearings. In modelling with cavitation, the maximum hydrodynamic pressure and load cmarrying capacity that the journal bearing is capable of relying on has a fairly rapid increase. The modelling results also relate to the friction force that occurs in the journal bearing.
Downloads
References
Hory, “Hydrodinamic Lubrication,” October, 2006.
Rasep, Zuraidah, Muhammad Noor Afiq Witri Muhammad Yazid, Syahrullail Samion, and Nor Azwadi Che Sidik. "Potential of RBD Palm Oil as a Lubricant in Textured Journal Bearing using CFD with Consideration of Cavitation and Conjugate Heat Transfer." CFD Letters 14, no. 2 (2022): 98-110. https://doi.org/10.37934/cfdl.14.2.98110
Syafaat, Imam, Luky Rika Sari, Muchammad Muchammad, Mohammad Tauviqirrahman, Eflita Yohana, Jamari Jamari, and Budi Setiyana. "Numerical Study of Comparison of Thrust Bearing Slip-No Slip Condition on Acoustic Performance." CFD Letters 15, no. 9 (2023): 1-17. https://doi.org/10.37934/cfdl.15.9.117
R. C. Juvinall, Fundamentals of Machine Component Design Fifth Edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2012.
Bayada, Guy, and Marie-Hélène Meurisse. "Impact of the cavitation model on the theoretical performance of heterogeneous slip/no-slip engineered contacts in hydrodynamic conditions." Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology 223, no. 3 (2009): 371-381. https://doi.org/10.1243/13506501JET476
Samanta, Pranab, S. Pradhan, and N. C. Murmu. "Thermal Analysis of Textured Journal Bearing Using Computational Fluid Dynamic Technique." International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) Vol 2: 2378-2383.
Androva, Althesa, Muhammad Tuviqirrahman, Nazaruddin Sinaga, Muhammad Khafidh, and Muhammad Sagaf. "Analysis of hydrophobic coating on load carrying capacity of journal bearing considering turbulence effect using CFD FSI method." In AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 2706, no. 1. AIP Publishing, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0120603
Versteeg, Henk Kaarle, and Weeratunge Malalasekera. An introduction to computational fluid dynamics: the finite volume method. Pearson education, 2007.
J.H.Ferziger and M.Peric, Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics, Third, Rev. Stanford: Springer.
Gropper, Daniel, Ling Wang, and Terry J. Harvey. "Hydrodynamic lubrication of textured surfaces: A review of modeling techniques and key findings." Tribology international 94 (2016): 509-529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2015.10.009
Tauviqirrahman, Mohammad, Paryanto Paryanto, Harry Indrawan, Nur Cahyo, Arion Simaremare, and Siti Aisyah. "Optimal Design of Lubricated Journal Bearing Under Surface Roughness Arrangement." In 2019 International Conference on Technologies and Policies in Electric Power & Energy, pp. 1-5. IEEE, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEECONF48524.2019.9102566
Tauviqirrahman, Mohammad, J. Jamari, Muhammad Bagir, Wahyu Caesarendra, and P. Paryanto. "Elastohydrodynamic behavior analysis on water-lubricated journal bearing: A study of acoustic and tribological performance based on CFD-FSI approach." Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering 44 (2022): 1-19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-021-03314-9
Navier, Claude. Mémoire sur les lois du mouvement des fluides. éditeur inconnu, 1822.
Spikes, Hugh, and Steve Granick. "Equation for slip of simple liquids at smooth solid surfaces." Langmuir 19, no. 12 (2003): 5065-5071. https://doi.org/10.1021/la034123j
M. Sagaf, N. Sinaga, M. Tauviqirrahman, M. Khafidh, and A. Androva, “Analysis of the journal bearing performance considering artificial surface roughness and cavitation using CFD FSI method,” AIP Conf. Proc., vol. 2706, no. May, 2023, doi: 10.1063/5.0120464. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0120464
Shi, Xi, and Ting Ni. "Effects of groove textures on fully lubricated sliding with cavitation." Tribology International 44, no. 12 (2011): 2022-2028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.08.018
Wang, Li‐li, and Chang‐hou Lu. "Numerical analysis of spiral oil wedge sleeve bearing including cavitation and wall slip effects." Lubrication science 27, no. 3 (2015): 193-207. https://doi.org/10.1002/ls.1267
Dobrica, M. B., M. Fillon, M. D. Pascovici, and T. Cicone. "Optimizing surface texture for hydrodynamic lubricated contacts using a mass-conserving numerical approach." Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology 224, no. 8 (2010): 737-750. https://doi.org/10.1243/13506501JET673
Sauer, Jürgen, and G. H. Schnerr. "Development of a new cavitation model based on bubble dynamics." ZAMM‐Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics/Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik 81, no. S3 S3 (2001): 561-562. https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.20010811559
Zwart, Philip J., Andrew G. Gerber, and Thabet Belamri. "A two-phase flow model for predicting cavitation dynamics." In Fifth international conference on multiphase flow, Yokohama, Japan, vol. 152. 2004.
Cupillard, Samuel, Sergei Glavatskih, and M. J. Cervantes. "Computational fluid dynamics analysis of a journal bearing with surface texturing." Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology 222, no. 2 (2008): 97-107. https://doi.org/10.1243/13506501JET319
Hamrock, Bernard J., Steven R. Schmid, and Bo O. Jacobson. Fundamentals of fluid film lubrication. CRC press, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203021187