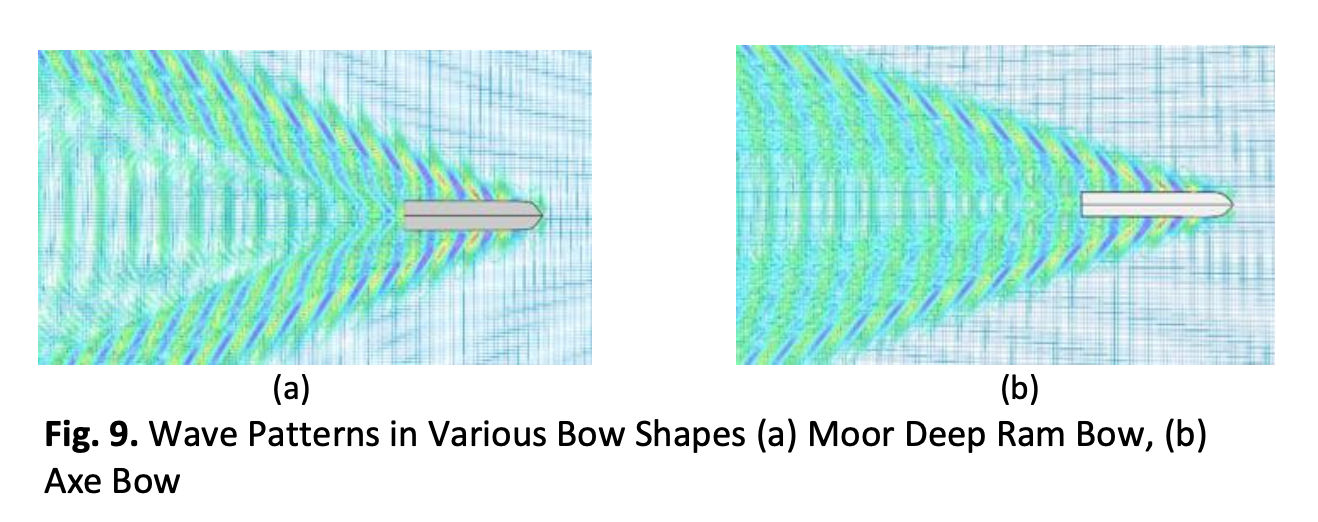
Comparative Study of Ship Resistance and Fuel Consumption between Axe Bow and Moor Deep Ram Bow using CFD Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/cfdl.14.8.7180Keywords:
Axe Bow, Bulbous Bow, CFD, Moor Deep Ram Bow, Ship ResistanceAbstract
Using a bulbous bow on the ship is the most common alternative way used to reduce resistance and fuel consumption. Some developments are created in terms of bow shapes to obtain the minimum shipping cost. The purpose of this study is to compare the total resistance (Rt) and specific fuel oil consumption (SFOC) in an 8000 DWT oil tanker by modifying the existing moor deep ram bow to axe bow using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and empirical Holtrop method. Based on the results, the total resistance with a moor deep ram bow design at a service speed of 12 knots is 230,8 kN, while axe bow is 221,5 kN. This is directly proportional to the fuel consumption where by using axe bow, the ship will consume 83.64 tons in a trip of 1912 nautical miles. In contrast, with existing moor deep ram bow, the fuel consumption is just a slight 0.1 % higher than axe bow and still showing a competitive performance as it is generally used in cargo vessel.
Downloads
References
Hakim, Muhammad Luqman, Bagus Nugroho, Rey Cheng Chin, Teguh Putranto, I. Ketut Suastika, and I. Ketut Aria Pria Utama. "Drag penalty causing from the roughness of recently cleaned and painted ship hull using RANS CFD." CFD Letters 12, no. 3 (2020): 78-88. https://doi.org/10.37934/cfdl.12.3.7888
Budiyanto, Muhammad Arif, Muhammad Aziz Murdianto, and Muhamad Fuad Syahrudin. "Study on the resistance reduction on high-speed vessel by application of stern foil using cfd simulation." CFD Letters 12, no. 4 (2020): 35-42. https://doi.org/10.37934/cfdl.12.4.3542
Hudson, Dominic A., Anthony F. Molland, and Stephen R. Turnock. Ship Resistance and Propulsion: Practical Estimation of Propulsive Power. Cambridge University Press, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511974113
Luo, Weilin, and Linqiang Lan. "Design optimization of the lines of the bulbous bow of a hull based on parametric modeling and computational fluid dynamics calculation." Mathematical and Computational Applications 22, no. 1 (2016): 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca22010004
Zha, Ruosi, Haixuan Ye, Zhirong Shen, and Decheng Wan. "Numerical study of viscous wave-making resistance of ship navigation in still water." Journal of Marine Science and Application 13, no. 2 (2014): 158-166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-014-1248-8
U. S. N. A. United States Naval Academy, "Chapter 7 Resistance and Powering of Ships," p. 46.
Schneekluth, Herbert, and Volker Bertram. “Ship design for efficiency and economy.” 218. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann 218, (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-7506-4133-3.X5000-2
Watson, David GM. “Practical ship design”. Elsevier 1 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1571-9952(98)80002-0
Kusuma, C., I. M. Ariana, and B. Ali. "Redesign KCR 60m Bow with Axe Bow Type To Reduce Ship Resistance." In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, vol. 557, no. 1, p. 012033. IOP Publishing, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/557/1/012033
Utama, I. Ketut Aria Pria, and Ketut Suastika Sutiyo. "Experimental and Numerical Investigation into the Effect of the Axe-Bow on the Drag Reduction of a Trimaran Configuration." IJTech 12, no. 3, (2021): 527. https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v12i3.4659
Keuning, Lex JA, J. Pinkster, and F. Van Walree. "Further investigation into hydrodynamic performance of the axe bow concept." In TUDelft, Faculty of Marine Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Report 1319-P, Published in: WEMT/HSMV2002 Proceeding, 6th Symposium on High Speed Marine Vehicles, Castello di Baia, Italy, 18-20 September (2002) .
Mahmood, Shahid, and Debo Huang. "Computational fluid dynamics based bulbous bow optimization using a genetic algorithm." Journal of Marine Science and Application 11, no. 3 (2012): 286-294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-012-1134-1
Lu, Yu, Xin Chang, and An-kang Hu. "A hydrodynamic optimization design methodology for a ship bulbous bow under multiple operating conditions." Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics 10, no. 1 (2016): 330-345. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2016.1159987
Nazemian, A., and P. Ghadimi. "Automated CFD-based optimization of inverted bow shape of a trimaran ship: An applicable and efficient optimization platform." Scientia Iranica 28, no. 5 (2021): 2751-2768. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2020.56644.4833
Aksenov, A. A., A. V. Pechenyuk, and D. Vučinić. "Ship hull form design and optimization based on CFD." Towards Green Marine Technology and Transport (2015): 215-223. https://doi.org/10.1201/b18855-31
Onwuegbuchunam, Donatus Eberechukwu, Favour Chimobi Ogbenna, Nnaemeka Charles Ezeanya, and Kenneth Okechukwu Okeke. "Ship Hull Form Optimization: A Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Approach." Technology 5, no. 3 (2019): 43-49. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijtet.20190503.11
Fitriadhy, Ahmad, Nur Amira Adam, Izzati Pison, Mohd Asamudin A. Rahman, Mohd Azlan Musa, and Mohd Hairil Mohd. "COMPUTATIONAL INVESTIGATION INTO RESISTANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF A PUSHER-BARGE SYSTEM." Journal of Naval Architecture & Marine Engineering 18, no. 2 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3329/jname.v18i2.52593
Fitriadhy, A., S. A. Azmi, N. Aqilah Mansor, and N. Adlina Aldin. "Computational fluid dynamics investigation on total resistance coefficient of a high-speed" deep-V" catamaran in shallow water." International Journal of Automotive & Mechanical Engineering 14, no. 2 (2017). https://doi.org/10.15282/ijame.14.2.2017.18.0347
Bertram, Volker. "Practical ship hydrodynamics butterworth." (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-075064851-6/50003-5