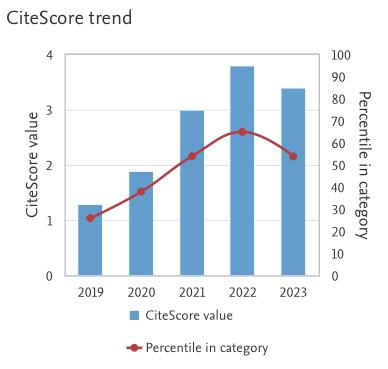
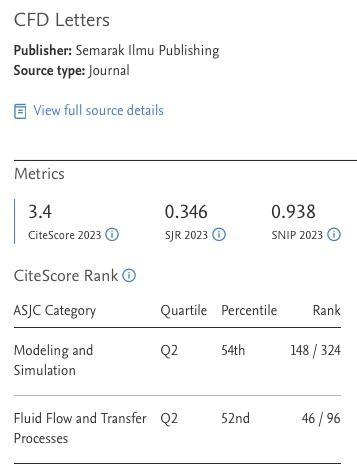
CFD Analysis on the Effects of Different Coal on Combustion Characteristics in Coal-Fired Boiler
Keywords:
Boiler, coal, combustion, furnace exit gas temperatureAbstract
Coal quality is essential for the optimum functioning of coal-fired power plants. One of
the issues associated with coal quality deterioration is poor combustion behaviour
which could result in ash deposition and environmental issues. This paper presents a
CFD investigation of flow and combustion process in a full-scale furnace. Three
different sub-bituminous coals with different properties were tested namely Coal A, B
and C. The aim is to predict the combustion performance of these coals by observing
its flow, temperature and species concentration inside the furnace. The exact boiler
furnace geometry obtained from boiler operator was translated into CFD model with
very little modification made for optimizing mesh. Grid dependency test carried out
prior to the work shows the current mesh scheme is sufficient to accurately resolve the
flow field. The results of the study show that combustion temperature for Coal B is the
highest at approximately 1400°C. Coal C is predicted to give the highest velocity peak
at certain regions of the furnace and interestingly enough, the same coal shows the
shortest flame length and thus requiring additional flow to achieve the same
penetration compared to other coals. Tracing of oxygen concentration inside the
furnace show minimum oxygen left in the rear pass given by Coal A, indicating optimum
combustion.