Comparative Analysis of Fuzzy Logic, PID, and FOPID Controllers in DC Microgrid Voltage Regulation for Power Plants: Integrating Renewable Energy Sources
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.128.1.5061Keywords:
DC microgrid voltage regulation, renewable energy integration, PID controllers, fuzzy logic controllers, Fractional Order PID (FOPID) controllersAbstract
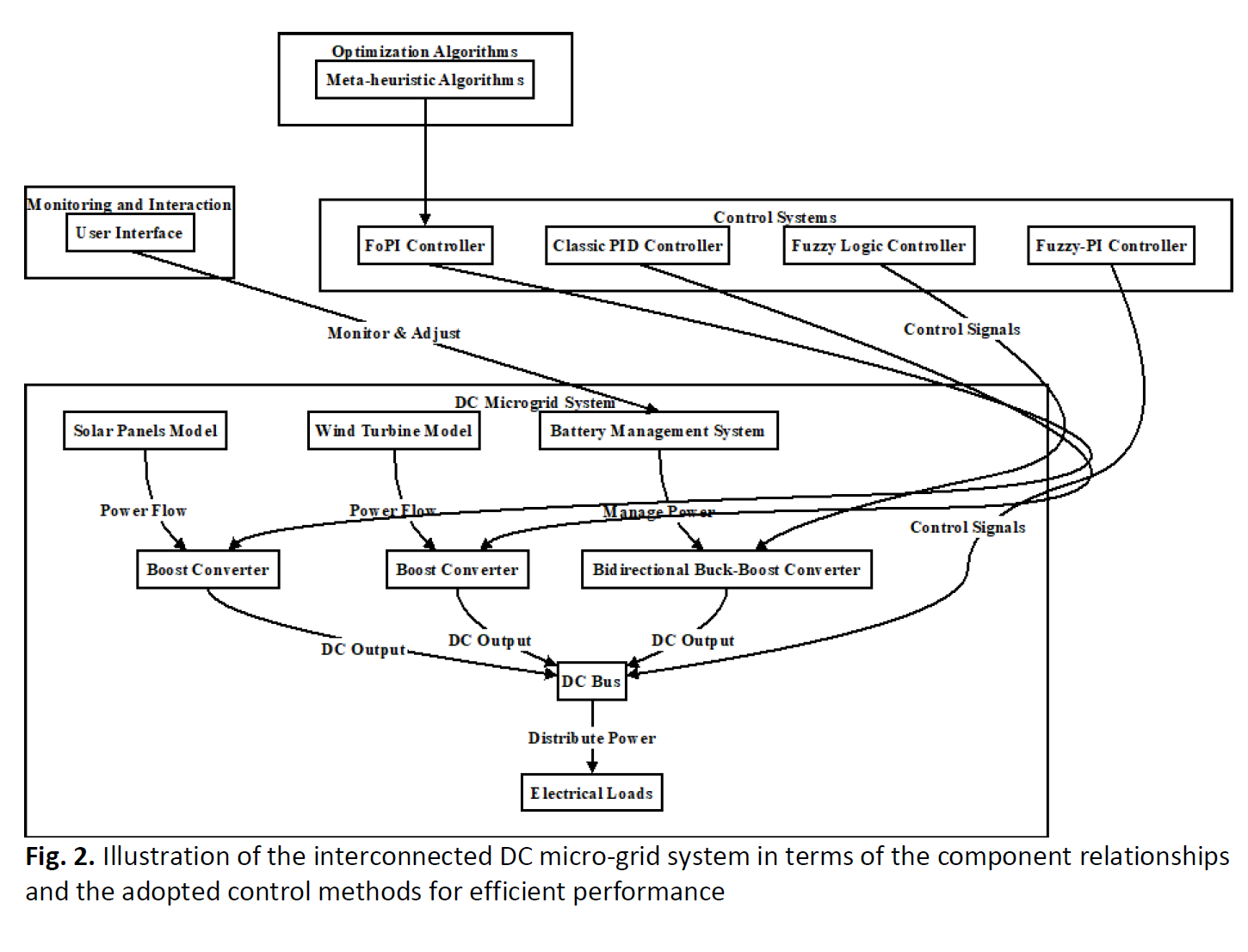
The worldwide direction moving towards sustainable energy solutions requires more advanced control mechanisms within power systems, especially in DC microgrids that combine renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines with conventional power setups. This paper addresses the necessary challenge of maintaining steady and efficient DC voltage control—important for the dependability and performance of power plants. Specifically, it looks at the efficiency of four different control strategies: classic PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers, Fuzzy Logic Controllers (FLC), Fractional Order PID (FOPID) controllers, and a new mixed system that merges Fuzzy Logic with PID controllers in a Fuzzy-PI layout. Our approach utilizes a strict comparative analysis using MATLAB Simulink simulations, assessing each controller’s capacity to manage dynamic load shifts, adjust to the unpredictability of renewable energy inputs, and preserve strong voltage stability under various operational cases. The simulations are crafted to single out the most effective control strategy to boost efficiency and toughness in microgrid operations. This study adds substantially to the progress of control strategies in hybrid energy systems, offering important insights into the creation of more complex and reliable power management solutions. By evaluating the performance of these varied controllers, we aim to underline potential upgrades in control systems that could support better energy management in intricate grid setups, thereby encouraging the wider inclusion of renewable energy technologies into power grids.
Downloads