Photodegradation Mechanism of Biopolymer Blended with High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.103.1.112Keywords:
Synthetic polymer, biopolymers, blending polymer, photodegradation mechanismAbstract
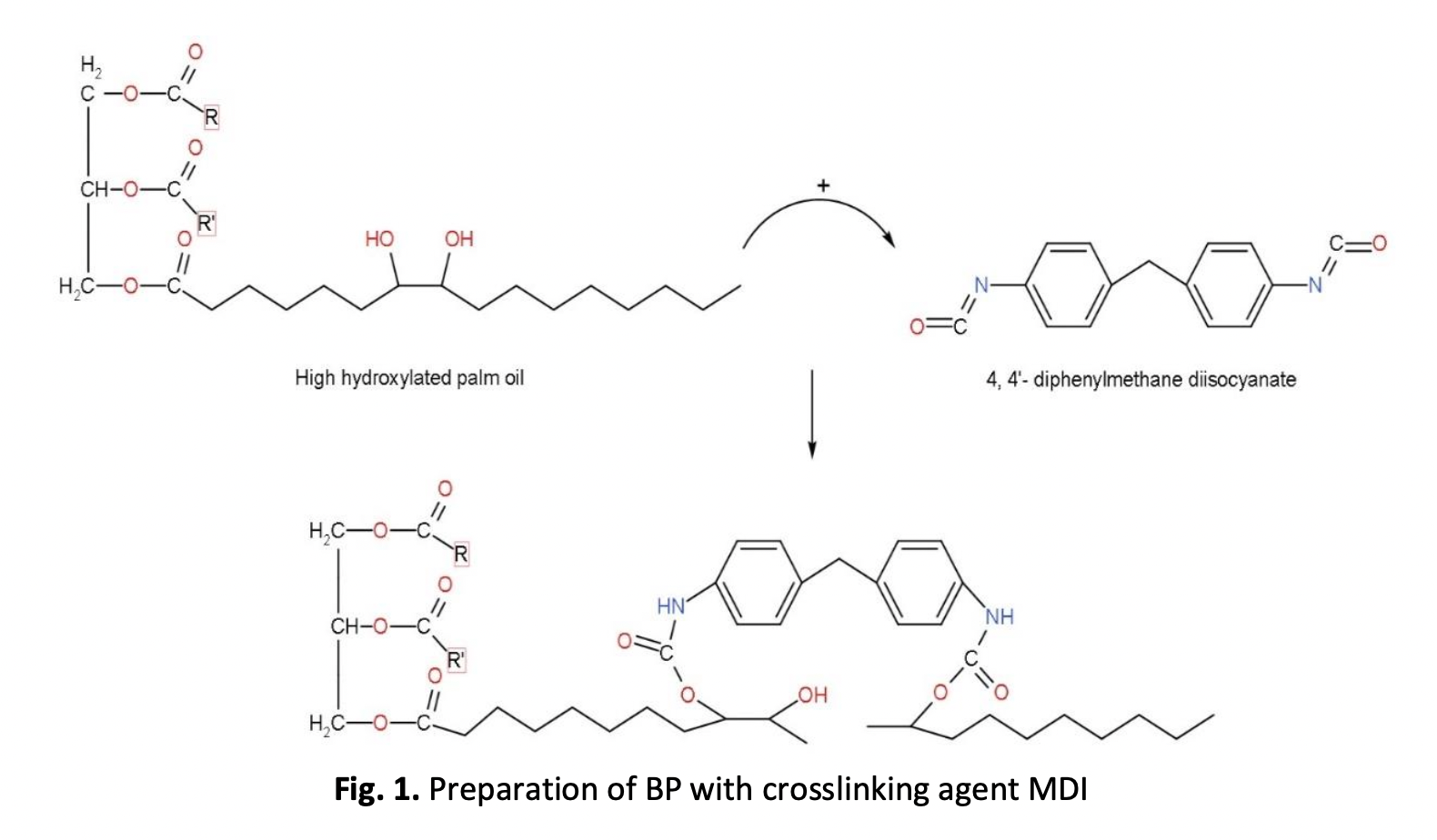
Synthetic polymer such as polyethylene is used widely in industry, agricultures and daily life owing to its relatively low price and good mechanical and processing properties. These synthetic polymers are, however, often not environmentally friendly because they typically do not undergo the process of biodegradation and, of course, are dependent on a limited petroleum resource. Therefore, concerns on environmental problems caused using of non-degradable petrochemical polymers have caused an increasing interest in degradable polymers especially biopolymers from crop plants. Biopolymers have much potential and several advantages, but they possess some drawbacks as well. Despite increasing production capacity, they are still quite expensive compared to commodity polymers and their properties are also often inferior, or at least do not correspond to the expectation of converters or users. This concept has led to the development blending of biopolymer and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE). In this study, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30% of Biopolymer (BP) was blended with HDPE known as BBP5, BBP10, BBP15, BBP20, BBP25 and BBP30 were prepared by melt-mixing process by using Brabender Plastograph® EC machine. BBP5, BBP10, BBP15, BBP20, BBP25 and BBP30 then were exposed in UV weatherometer by using UV Lamp Test Chamber Model HD-703 at different UV exposure, which is 250h, 500h, 750h,1000h, 2000h, and 3000h. Physical properties and photodegradation mechanism development of BBP5, BBP10, BBP15, BBP20, BBP25 and BBP30 were examined by means of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) at different UV exposure. The photodegradation mechanism of BBP5, BBP10, BBP15, BBP20, BBP25 and BBP30 shows relationship with the Norrish type I and Norrish type II reaction as indicated the possibilities of blended polymer degradation process was occurred.
Downloads