Effects of Coating and Lubrication on Friction and Wear for Metal-to Metal Application
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.110.1.5262Keywords:
Block on ring test, coefficient of friction, wear volume lossAbstract
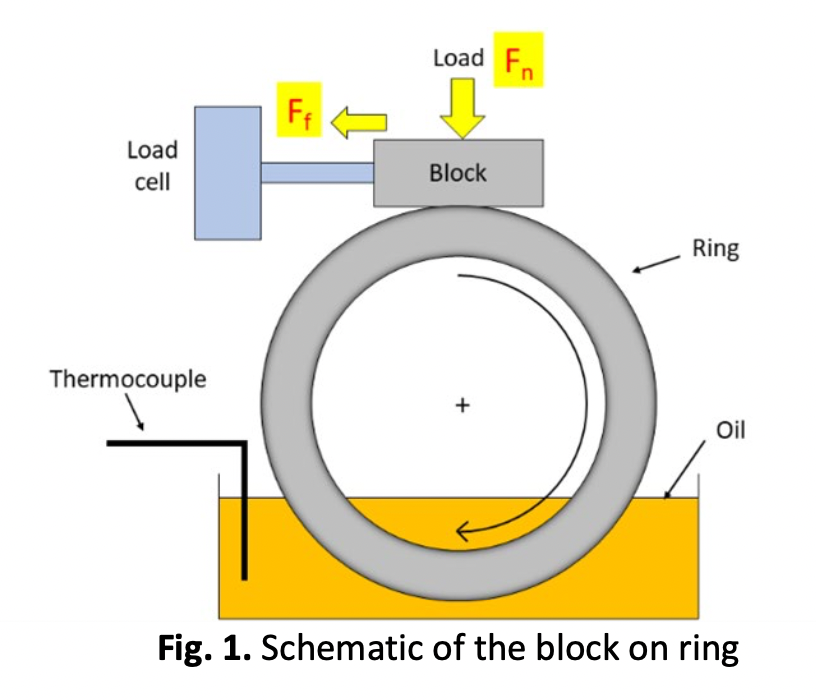
Friction and wear between sliding surfaces can lead to various issues in industrial applications, such as increased costs, reduced machine lifespan, loss of functionality, energy loss, and decreased system efficiency. To mitigate these problems, lubricants and coatings are commonly employed. This study aims to investigate the impact of coatings and lubrication on friction coefficient, wear volume loss, and lubricant temperature using the block-on-ring wear test. The effectiveness of different coatings (uncoated, DLC, CrN, and TiALN) and lubricants (anti-friction graphene oxide additive oil and strong nano engine oil additive) in reducing friction and wear is evaluated. The block-on-ring tests are conducted under varying loads (6-60 N), speeds (1450 rpm), lubricant volumes (40 ml), and durations (2-20 min). The coefficient of friction is measured using an inline load cell, wear volume loss is determined by weighing the blocks before and after the experiment, and lubricant temperature is monitored using thermocouples. The results indicate that the coefficient of friction decreases with increasing load, while the lubricant temperature rises. Coated blocks exhibit lower wear volume loss compared to uncoated blocks. Overall, the combination of CrN-coated blocks and anti-friction graphene oxide additive oil demonstrates the best tribological performance.
Downloads