The Exploration of the Characteristics of Concrete Incorporating Ultrafine Coal Bottom Ash and Spent Garnet
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.36.2.164175Keywords:
Ultrafine CBA, Spent garnet, ConcreteAbstract
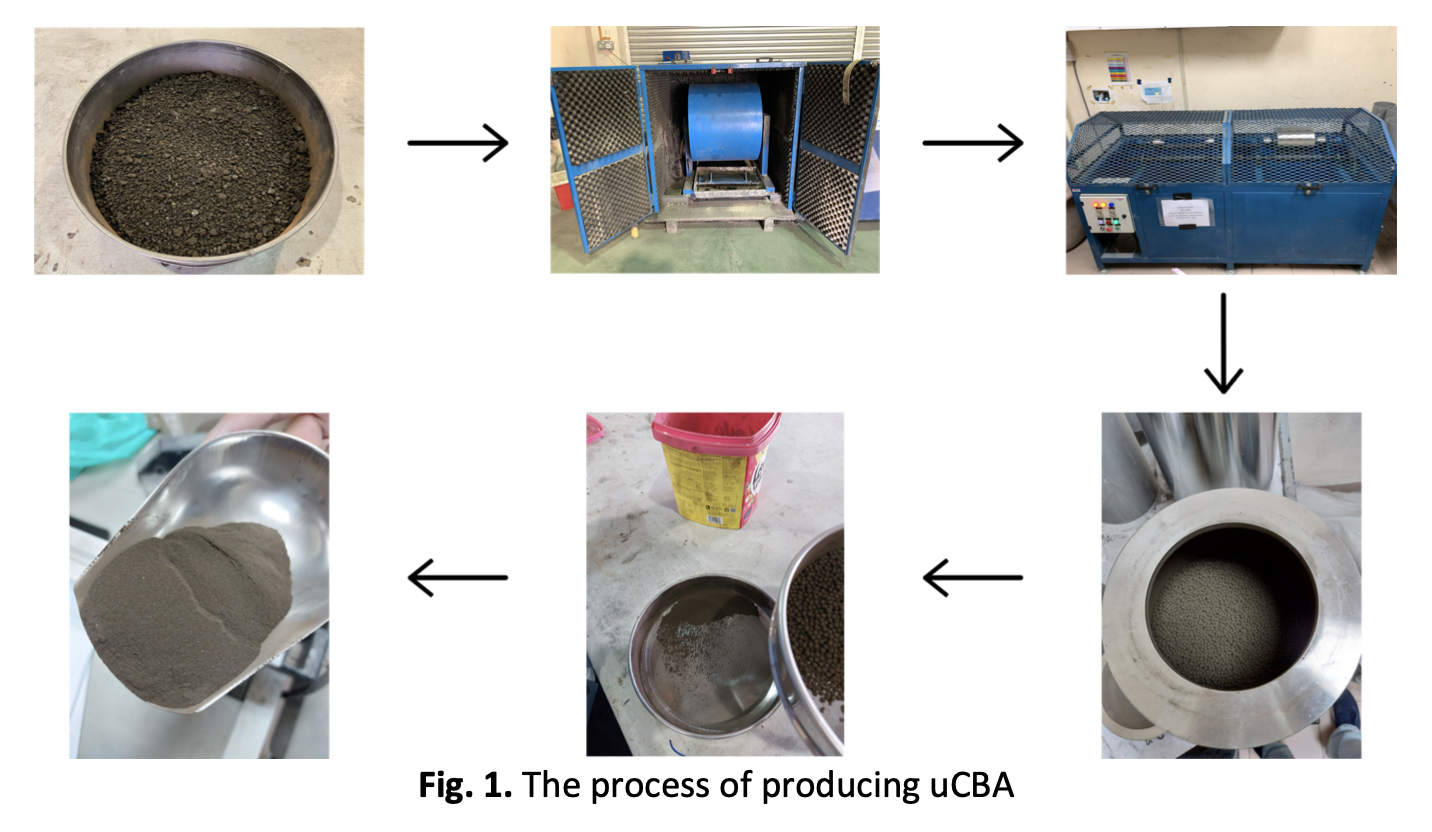
The building sector is a significant contributor to global carbon emissions, primarily due to the production of cement, a crucial construction material. The need for sustainable building practices has spurred research into alternative materials to traditional cement and sand. Two such materials, ultrafine coal bottom ash (uCBA) and spent garnet (SG), have shown potential as substitutes for cement and fine aggregate, respectively. This research examines the effectiveness of uCBA as a partial replacement for cement and SG as a partial replacement for fine aggregate in concrete, at varying levels of 3%, 6%, and 9% for uCBA and 10%, 20%, and 30% for SG. Initially, the chemical composition analysis was conducted using an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF), and the particle morphology of uCBA, OPC, and SG was examined through field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). Then, the study evaluates the performance of these materials based on slump value, compressive strength, and splitting tensile strength, with specimens undergoing 28, 56, and 90-day curing periods. Results indicate that integrating uCBA and SG in concrete at levels of 3% and 10%, respectively, enhances compressive and splitting tensile strength while decreasing environmental impact. Moreover, workability improves with higher substitution levels. Overall, this research indicates that uCBA and SG hold great potential as replacements for cement and fine aggregate in concrete, providing a means to mitigate the environmental impact of construction.
Downloads