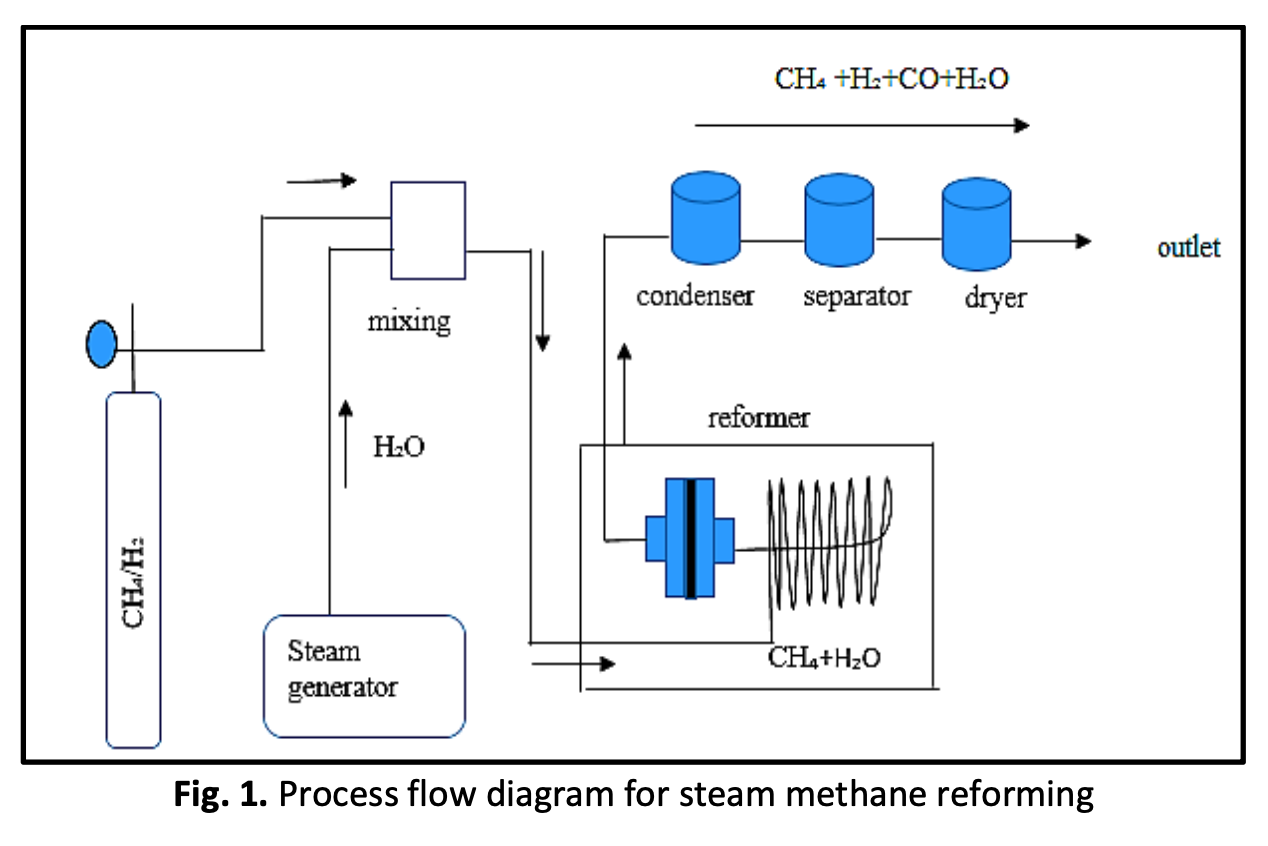
Producing the Methane Conversion by Steam Methane Reforming Over SiO2-NiO Catalyst
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.99.1.2834Keywords:
Sintering, silica, nickel, rice husk, foams, slurry methodAbstract
Methane is the main compound of natural gas and is today used in various industrial processes and also as energy source in gas turbines or natural gas fuelled vehicles. Methane is considered a substantially more potent greenhouse gas than CO2. This study presents an approach for the catalyst of SiO2-NiO foam in steam methane reforming. The 35 wt.% composition of Silica (SiO2) that produced from Rice Husk Ash (RHA) was used in this study by using slurry technique to produce of SiO2-NiO foam at 950°C and 1250°C of sintering temperatures. The morphologies of SiO2 -NiO foams were observed by using the Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) to identify the pore size as a catalyst filter. The pore size of SiO2-NiO foam were found in the range 13µm to 43µm. SiO2-NiO catalyst were characterized by temperature programmed reduction (TPR). The TPR result showed present of SiO2-NiO was successfully activated at the 320°C at 30 minutes. Meanwhile, in the temperature range of 500°C–600°C, the catalyst was shown to be particularly active and stable. The high methane conversion 42% was produced at the reaction temperature of 600°C.
Downloads