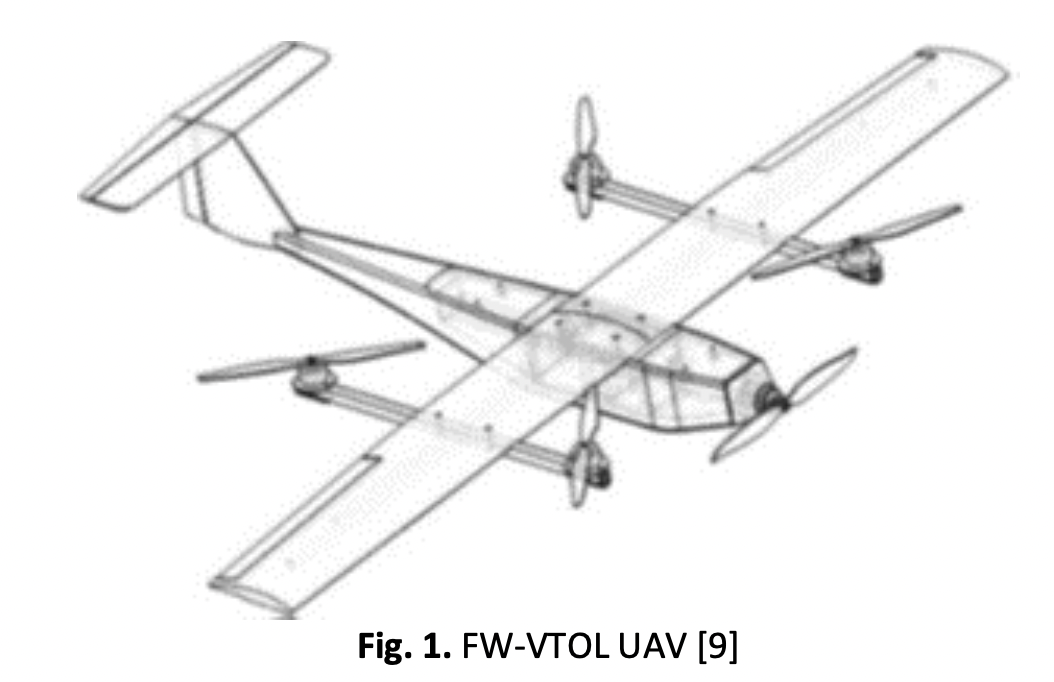
Design and Aerodynamic Analysis of Fixed-Wing Vertical Take-Off Landing (FW-VTOL) UAV
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.106.1.136146Keywords:
Fixed wing, VTOL, aerodynamic characteristicsAbstract
This study aims to produce a Fixed Wing-Vertical Takeoff Landing (FW-VTOL) design that has good aerodynamic characteristics on its wing and fuselage. The design process begins with determining the Design Requirement and Objective (DRO). According to DRO, the aircraft is designed to be able to operate at speeds of 14 m/s and an altitude of 120 m (cruise phase) above ground level. The Maximum Takeoff Weight (MTOW) of the planned is estimated using previous research data. Based on calculations, for it to have a flight time of 30 minutes, the MTOW of the FW-VTOL is 5.2 kg. The fuselage and wing of the FW-VTOL design were carried out by referring to the MTOW of 5.2 kg. Three candidate airfoils were proposed, and their aerodynamic characteristics were determined using XFLR5 software. The aerodynamic characteristics of the three proposed fuselage candidates are also calculated. At an angle of attack of 30, the Eppler 66 airfoil produces the most lift coefficient and the lift-to-drag ratio of 0.8775 and 94.152, respectively. While the NACA 4412 and S9000 airfoils create lift coefficients of 0.7963 and 0.7963, respectively. From the calculation of aerodynamic characteristics, the first, second, and third fuselage candidates produce drag coefficient values of 0.1397, 0.1576, and 0.1368, respectively. The aerodynamic characteristics of the airfoil and fuselage are then input into the decision matrix table. As a result, the selected airfoil candidate is Eppler 66, while we choose the fuselage design is the third fuselage candidate.
Downloads