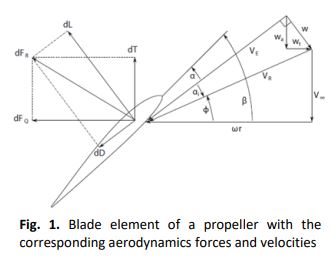
Experimental Test on Aerodynamic Performance of Propeller and its Effect on the Flight Performance of Serindit V-2 UAV
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.91.2.120132Keywords:
Aerodynamic performance, serindit V-2, UAV, flight testAbstract
The Serindit V-2 is a flying vehicle (UAV) that was successfully developed to participate in the Indonesian Flying Robot Contest with a mission to fly at high speed and acceleration. The purpose of this research is to obtain the optimum aerodynamic performance of the propeller and its effect to the flight performance of the Serindit V-2 Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV). The study began by testing the aerodynamic performance of propellers (static thrust value, time consumed, and power consumed) with different sizes of propellers, ranging from 8 inches to 12 inches. From the test results, the 12-inch propeller at 100% throttle generates the highest thrust value of 29.607 N, time consumed of 4.91 minutes, and power consumed of 717.57 Watt. The study was continued by calculating the flight performance with the results that the maximum speed value was 24.11 m/s, the rate of climb was 3.347 m/s, and the stall speed was 14.6 m/s. Finally, the Serindit V-2 UAV was tested to fly using a propulsion system with a 12-inch propeller and varied throttle opening from 50% to 100%. The test results show the vehicle's maximum speed of 24,562 m/s is obtained at a throttle opening of 100%. The climb rate and the flight time at 100% throttle opening is 2,656 m/s and 3 minutes 27 seconds, while the vehicle's stall speed during cruising flight (angle of attack at 1 degree) is 13 m/s. The difference between the theoretical calculation results and the actual test is at least caused by 2 factors. The first is the aerodynamic factor, in theoretical calculations, the overall aerodynamic design of the aircraft is considered very smooth/seamless. This has an impact on the fluid flow that occurs on the aircraft. On the actual conditions, the vehicle has several parts that cause drag, such as the pitot sensor located at the tip of the right-wing, and the ballast located on the left-wing.
Downloads