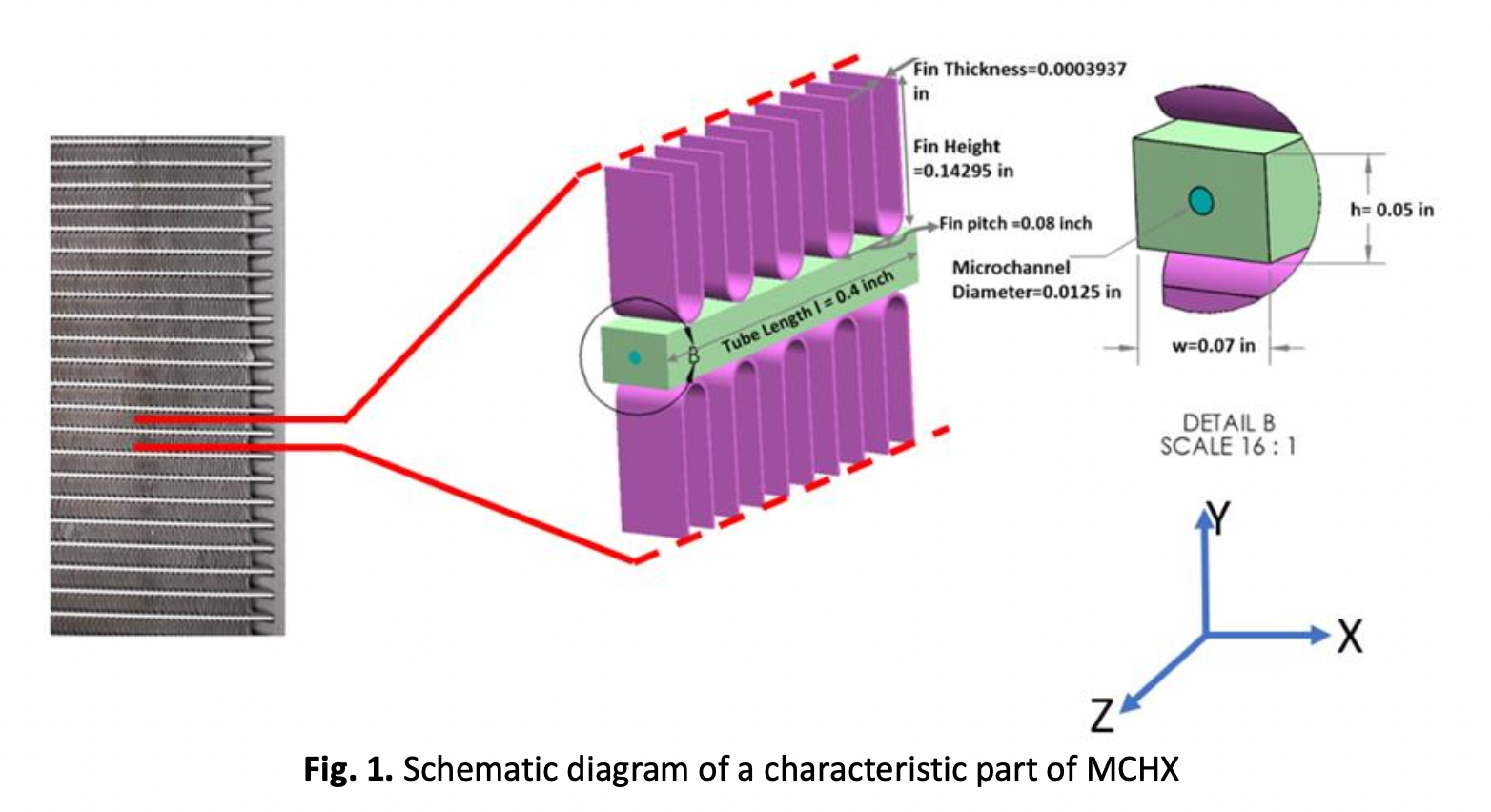
High-Fidelity Conjugate Heat Transfer Simulation of Micro-Channel Heat Exchanger
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.106.1.165181Keywords:
Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD), Microchannel Heat Exchanger (MCHE), conjugate heat transferAbstract
In this study, high-fidelity conjugate heat transfer simulations are used to model a micro-channel heat exchanger (MCHE) in a crossflow to study its thermal-hydraulic performance. Three different microchannel geometries, namely circular, triangular, and square with louver-shaped fins, are considered. The local flow field showed a strong coupling between the microchannel flow, solid domain, and crossflow. The flow separation and wake regions formed near MCHE resulted in a large variation in the velocity field and temperature in the crossflow. The interaction of the wake region with the fins introduces significant spanwise variations, leading to variations in the thermal boundary layer. The heat conduction in the solid structure provided a non-uniform temperature field with a higher temperature near the microchannel and a slightly lower temperature near the surface exposed to the crossflow. The microchannel flow analysis showed that the internal geometry affects the pressure drop, which is highest for the triangular MCHE and lowest for the circular MCHE. Based on the effectiveness and performance index calculations, the circular MCHE exhibited the best performance, while the rectangular MCHE showed higher heat transfer effectiveness.
Downloads