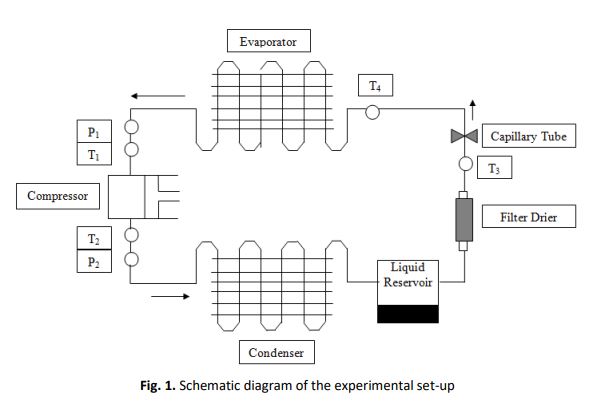
Experimental Performance of R134a/SiO2 in Refrigeration System for Domestic Use
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.95.1.145163Keywords:
Nanolubricant, nanorefrigerant, refrigeration system, heat transferAbstract
Nanofluids are considered as a new invention of fluids having superior thermal physical properties to improve efficiency of the refrigeration system. Nanofluids are the colloidal suspensions of nanoparticles in base fluid. Nanoparticles having higher thermal conductivity compared to pure refrigerant such as R134a can be added to pure refrigerant to improve the performance of refrigeration system. This study focuses on producing nanolubricant (SiO2/POE) and implementing the nanolubricant into refrigeration system. The nanoparticles will be homogenized in refrigerant to produce nanoRefrigerant (R134a/SiO2) at the attached reservoir. The aim of the research is to study the thermal physical properties of nanolubricant and to find the relationship between nanoparticles’ volume fraction to the Coefficient of Performance (COP) of the refrigeration system. The investigations are focused on the effects of nanoparticles with 0.1, 0.3%, 0.7% and 0.9% volume fraction to the performance of the refrigeration system. The results show that the usage of nanolubricant creates higher thermal conductivity with slightly higher dynamic viscosity which eventually increase the performance of the refrigeration system by 8.62% in term of COP.
Downloads