Investigating the Turbulent Flow around Semi-Circular Cylinder
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.112.2.191213Keywords:
Turbulent flow, semi-circular cylinder, drag coefficient, lift coefficient, skin frictionAbstract
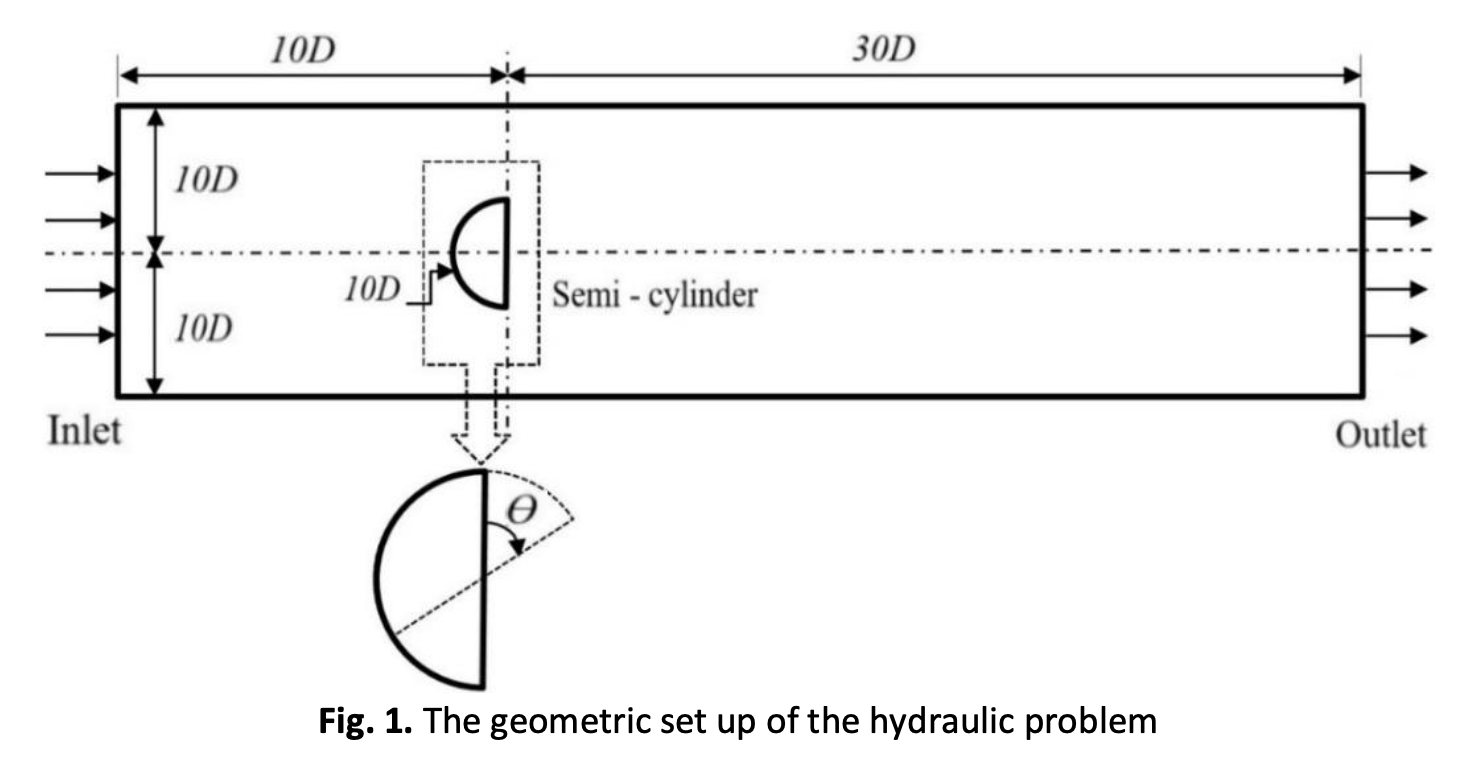
The Spalart-Allmaras turbulence model is used to study the flow patterns around a semi-circular cylinder surrounded by water in two dimensions with various angles of strike owing to rotating the cylinder by an angle. The rotation angle ranges from zero to 360° and the ANSYS Fluent software is employed to implement the required simulation. The Spalart-Allmaras turbulence model is used to determine the flow velocity vector, velocity contours, and pressure contours. Moreover, this turbulent model is used to calculate three different non-dimensional parameters, the drag coefficient, lift coefficient, and skin friction factors. Two different Reynolds numbers (Re) are adopted in the calculation of the three non-dimensional parameters with various values for the angle of the cylinder rotation. Here, the semi-circular cylinder is considered stationary but it is placed in a water domain in various positions. Due to the scarcity in information about using the Spalart-Allmaras turbulence model as compared with other models, which are widely used to investigate the flow around the cylinder, three turbulent models are employed to verify the results obtained by the Spalart-Allmaras model, these models are (standard), (RNG), and (Realizable). Results show an excellent agreement between the four turbulent models compared, where there is no significant variation in the obtained results, all results are very similar.
Downloads