Development of Portable Blood Carrier Box Employing Thermoelectric Module by Using Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch Composites as Materials of Box
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.93.2.5060Keywords:
Blood carrier box, thermoelectric cooler, coefficient of performancesAbstract
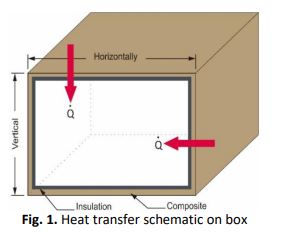
The process of blood distribution from the proper storage before transfusion requires a cooling unit, which is able to maintain the temperature of the blood and ensure that it is not damaged before being transfused. In order to maintain the chemical and structural composition of the blood, it should be stored at a temperature of 2-6 °C and distribution carried at a temperature of 2-10 °C with a maximum transit time of 24 hours specifically for whole blood. The cooling method currently used is by placing an ice pack or ice in a blood distribution room therefore, a special room, which prevents ice from cooling down, is continuously required for cooling. This study aims to design, manufacture and test a box that may be used as a means of blood transportation, does not require a special room to cool the cold room and works continuously for 2 hours. The thermoelectric cooler was chosen as a cooler in the blood carrier box because of its small size which makes it possible to be operated in a limited space and at a DC voltage of 12. Elements Peltier with type TEC1-12706 was use as the thermoelectric cooler and composites with oil palm empty fruit bunches, which has a thermal conductivity value of 0.13 W /m was chosen as the material for the box. The test carried out resulted in the highest coefficient of performance (COP) value, namely 0.168. The test was carried out at a voltage variation and loading of 9 volts and 7 blood bags of 350 ml, respectively. The result shows that the box is able to maintain a blood temperature of 2.65 °C and at the variation of the voltage and loading of 12 volts and 7 bags of 350 mL, respectively, it was able to maintain the best blood temperature of 2.62 °C.
Downloads