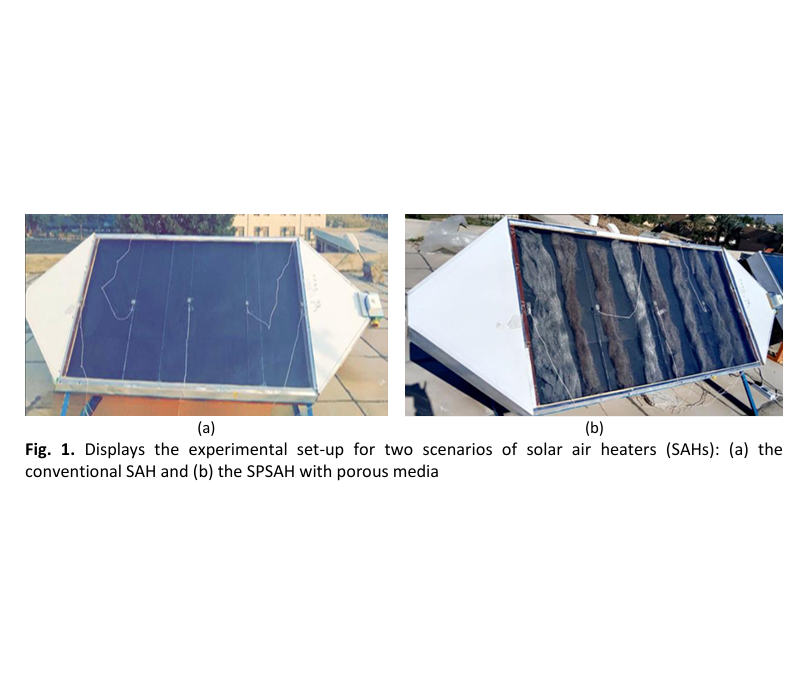
Experimental Study of the Effect of Porous Media on the Performance of Single-Pass Solar Air Heater
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.121.1.2738Keywords:
Solar energy, steel-wools, experimental approach, flat plate absorber, thermal efficiencyAbstract
Solar energy is harnessed to heat the air, which is then utilised for warming greenhouses and drying crops. Solar air heaters may readily increase their performance using an absorbent plate design with a front pass of steel wools. This kind of SAH has been investigated and compared to a conventional flat absorbent plate. Steel wool, a cost-effective and permeable substance, possesses excellent heat conductivity, and it can be utilised in ongoing initiatives to enhance convection and thermal efficiency. The analysis in this research is based on data from experiments, focusing on the single-pass SAH technique and considering two scenarios: traditional system and porous system, with air mass flow rates of 0.015 Kg/s and 0.035 Kg/s. The experimental findings show that employing porous materials increases the exhaust temp by 12.28% and 21.32 % form of air 0.015 and 0.035 Kg/s, respectively. Moreover, the solar radiation readings for non-porous and porous medium SAHs were recorded as 905.32-912.92 and 979.04-945.6 W/m2, respectively, at 1:30 p.m. Furthermore, thermal efficiency is between 33.29 % and 64.36 % in the porous scenarios and between 30.12% and 57.36% for non-porous cases. Porous media increases the thermal efficiency by 10 % and mass flow rate by 14 %.
Downloads