Water Absorption Study on Kenaf/ABS Composites
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.99.2.180186Keywords:
Water absorption, kenaf, ABS composites, morphology, natural fiberAbstract
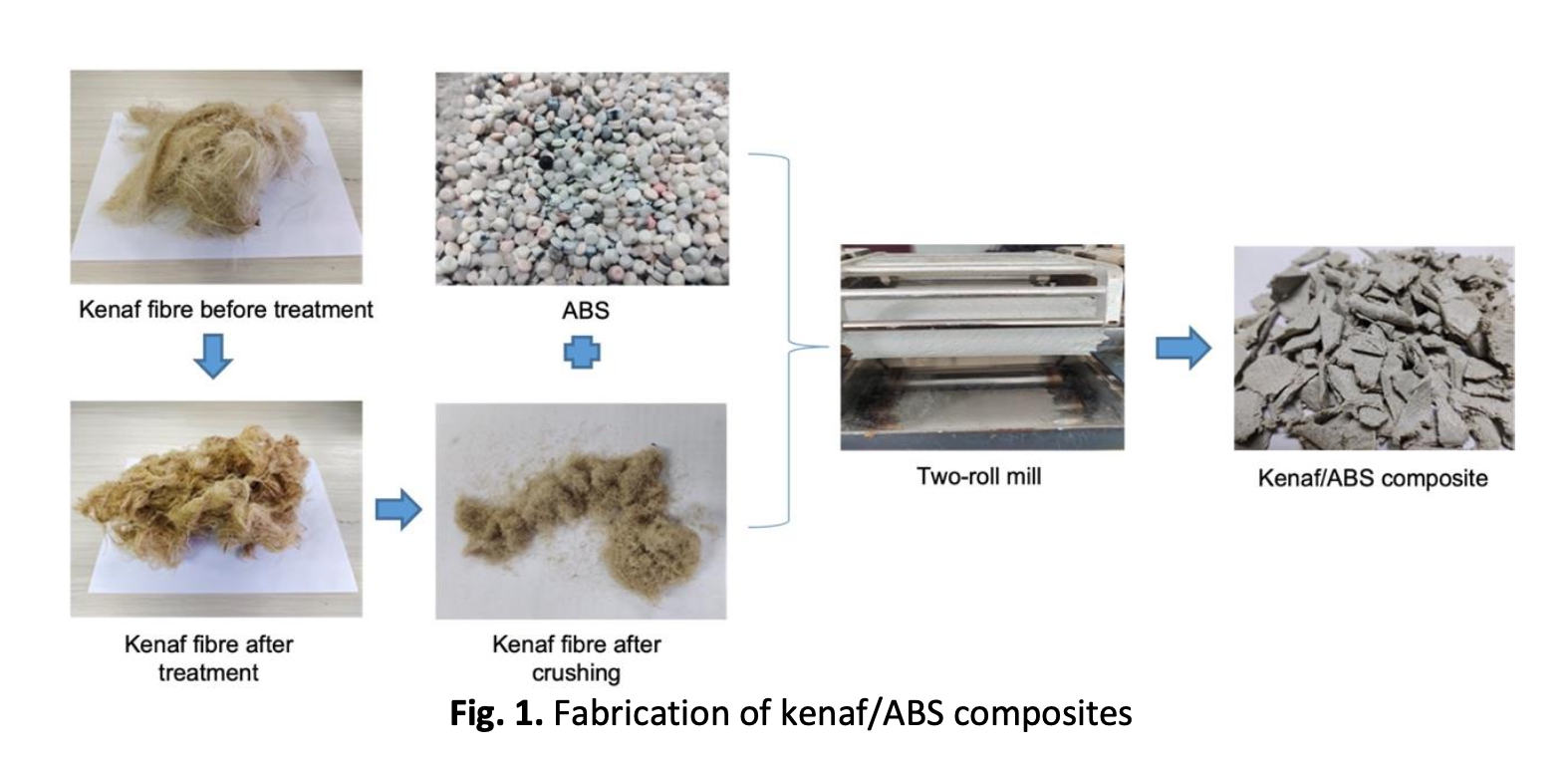
Many manufacturers have lately expressed an interest in the use of fiber-reinforced polymer composites (FRPs) in structural applications. Carbon and glass fibers, for example, have been commercialized globally for decades. However, they are harmful to the environment since synthetic fibers are non-biodegradable and difficult to recycle once they have fulfilled their purpose. As a result of their better physical and mechanical qualities, natural fiber composites such as kenaf are a prospective substitute for synthetic fiber. Kenaf is the most promising alternative for replacing synthetic fibers in order to achieve the environmental preservation while simultaneously exhibiting great properties such as equivalent specific strength, low density, and renewable resources. Treated kenaf fiber was added to ABS with varying loading (10, 15, 20 and 25 wt.%) via Two Roll Mill machine. The influence of the fiber on the composites was evaluated for water absorption properties. The water absorption test was conducted for 5 days referring to the ASTM D570. The morphology of produced composite was investigated using JOEL Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) at 200X magnifications. The incorporation of the treated kenaf fiber has an influence on the properties of kenaf/ABS composites. The fiber was well dispersed in the matrix and showed good adhesion to the ABS. Kenaf/ABS composites showed an increment of water absorbed with an increment of fiber loading.
Downloads