Effects of Evaporating Temperature on the Flow Pattern of Dimethyl Ether in a Horizontal Evaporator
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.100.1.4452Keywords:
Dimethyl ether, void fraction, flow pattern, evaporatorAbstract
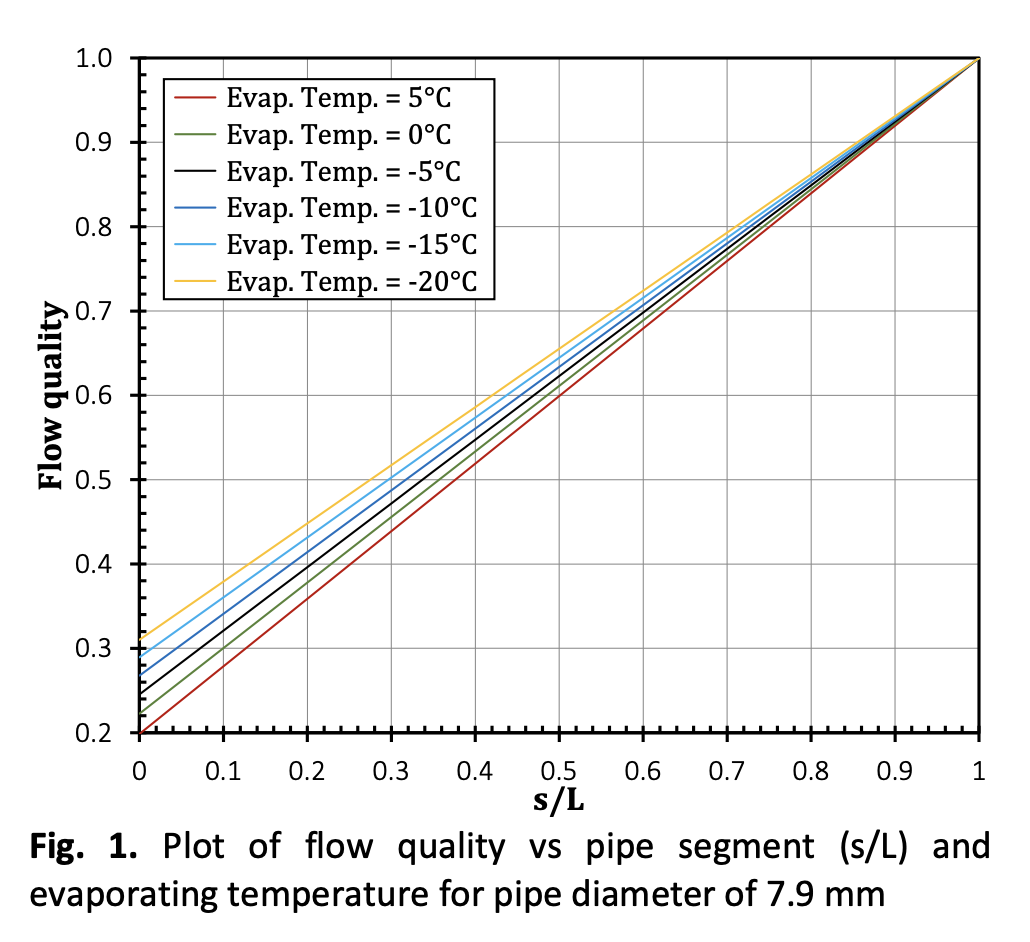
Dimethyl ether is one of the derivative products of coal that will be used as a household fuel substitute for LPG in Indonesia. In addition, it can also be used as a working fluid in a refrigeration system. To understand the behavior of this refrigerant, a simulation was carried out to determine the flow pattern of dimethyl ether in a horizontal evaporator. This study was applied in an evaporator of an air conditioner with inside diameter of 6.3 and 7.9 mm and cooling capacity of 2.64 and 5.28 kW. By varying the evaporation temperature from -20 to 5°C it was observed that the flow pattern was dominated by annular flow when the evaporation temperature was set at higher value. Simulation using pipe diameter of 7.9 mm and cooling capacity of 2.64 kW showed that at the evaporator inlet the flow pattern is combination of stratified-wavy and wavy-annular for all range of evaporation temperature. When the pipe diameter was reduced to 6.3 mm, stratified wavy at the evaporator inlet was only found at evaporating temperature of -15 and -20°C. All stratified wavy flow vanishes when the cooling capacity was doubled to 5.28 kW. Annular flow is dominant under this condition.
Downloads