Heat and Mass Transfer Characteristics of Mixed Convection MHD Flow with the Impacts of Hall Current and Diffusion Thermo in the Presence of Brownian Motion and Thermophoresis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.115.1.5168Keywords:
Hybrid nanofluids, chemical reaction, stretching plate, rotation parameter, Hall current, boundary layerAbstract
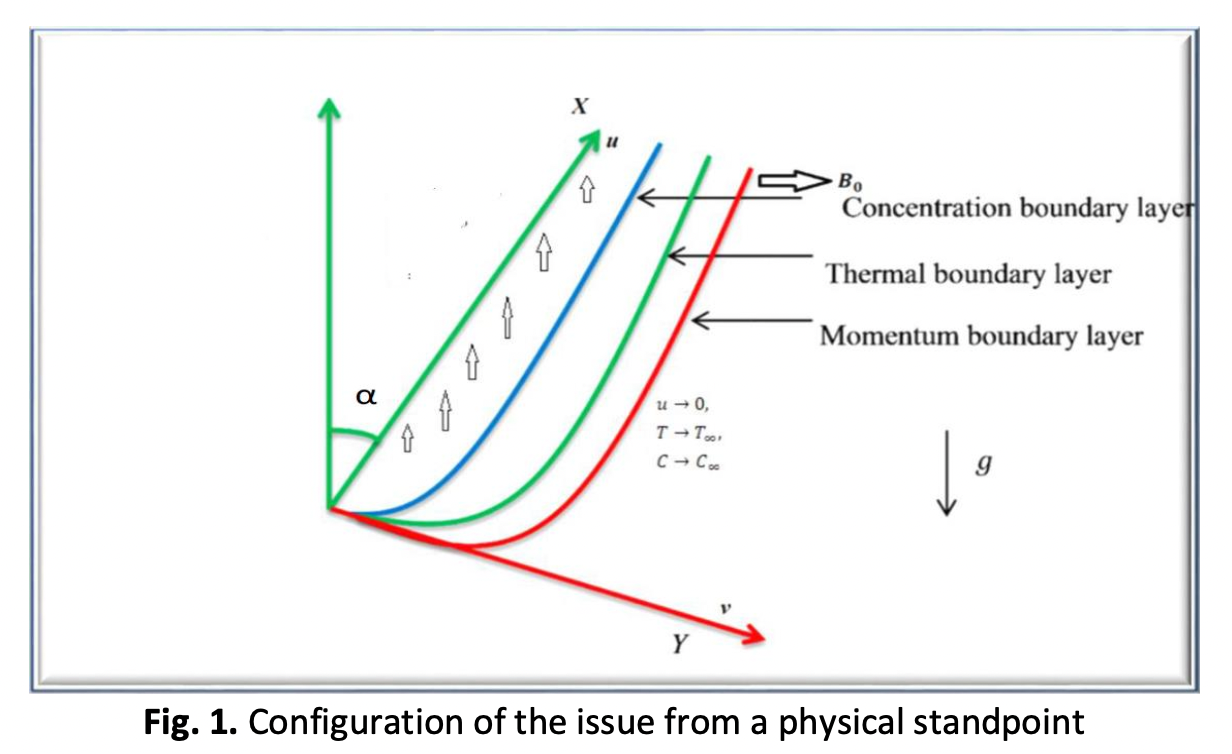
This study investigates the influence of Hall current diffusion, thermo-activation energy, and other parameters on the flow characteristics of an electrically conducting Jeffrey nanofluid. The Jeffrey nanofluid flow occurs across a continually expanding surface, and additional factors like thermal radiation, heat generation/absorption, and inclined plates are included in the analysis. A vertically installed transverse magnetic field is assumed to have a modest Reynolds number. The controlling partial differential equations are transformed into nonlinear ordinary differential equations using appropriate similarity transformations. These equations are then numerically solved using the Matlab bvp4c module. This study aims to analyze the impact of many factors, including the Hall current factor, the thermal radiation factor, the heat source/sink factor, the Brownian motion factor, the thermophoresis parameter, and the magnetization, on the velocity, concentration, and temperature. To do this, graphical representations will be used as a means of visualizing and discussing the impacts, as mentioned earlier. To get a deeper understanding of the internal dynamics of the emerging parameters, a numerical computation is conducted to determine the local Nusselt number, Sherwood number, and skin friction coefficient along the x and z axes. Research findings have shown that the flow velocity exhibits a decreasing trend as the linear and nonlinear thermal radiation components rise. Furthermore, augmenting the values of the Brownian motion parameter will lead to a reduction in the concentration profile of the nanoparticle.
Downloads