Influence of ZnO Dopant on Piezoelectric Properties of Potassium Sodium Niobate Thin Films
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.111.1.153160Keywords:
Piezoelectric, Lead-free, KNNAbstract
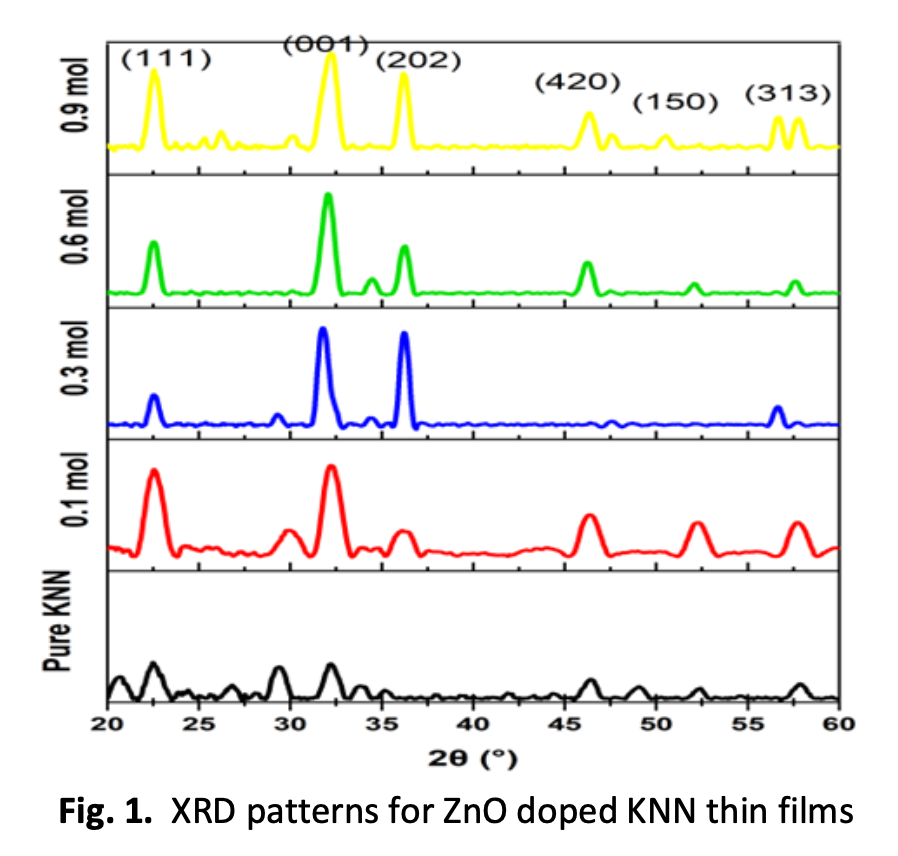
Lead zirconia titanate (PZT) is widely used due to its ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties. However, toxic lead in PZT is extensively linked to the greenhouse effect. For this constraint, extensive research is being done to find new piezoelectric materials such as potassium sodium niobate (K0.5Na0.5NbO3 or KNN). Due to processing difficulties, KNN has been disregarded for a long time. Volatilization of alkaline elements causes compositional inhomogeneity and lowers piezoelectric activity of ceramics. This research examines how ZnO-doping affects the structural and electrical changes and characteristics of potassium sodium niobate (KNN) ceramics. Potassium Sodium Niobate (KNN) thin films were grown on ITO substrate by using sol-gel spin coating method. The as-deposited thin films were heated 250 ℃ pyrolysis for 5 min and then was annealed at the temperature 650 ℃. Following this, KNN thin films were characterized using X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM). The electrical properties of KNN thin films were analysed using Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and Piezoresponse Force Microscopy (PFM). Based on the findings, it can be inferred that a doping concentration of 0.9 mol ZnO is considered the most appropriate for the production of a homogeneous and cohesive KNN thin film. This film demonstrates favourable electrical properties, making it well-suited for implementation in piezoelectric applications.
Downloads