Electrodeposited Bismuth Telluride Nanocomposite Thermoelectric Film with Improved Graphene Deposition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.111.1.161172Keywords:
Thermoelectric film, electrodeposition, bismuth telluride, graphene, nanocompositeAbstract
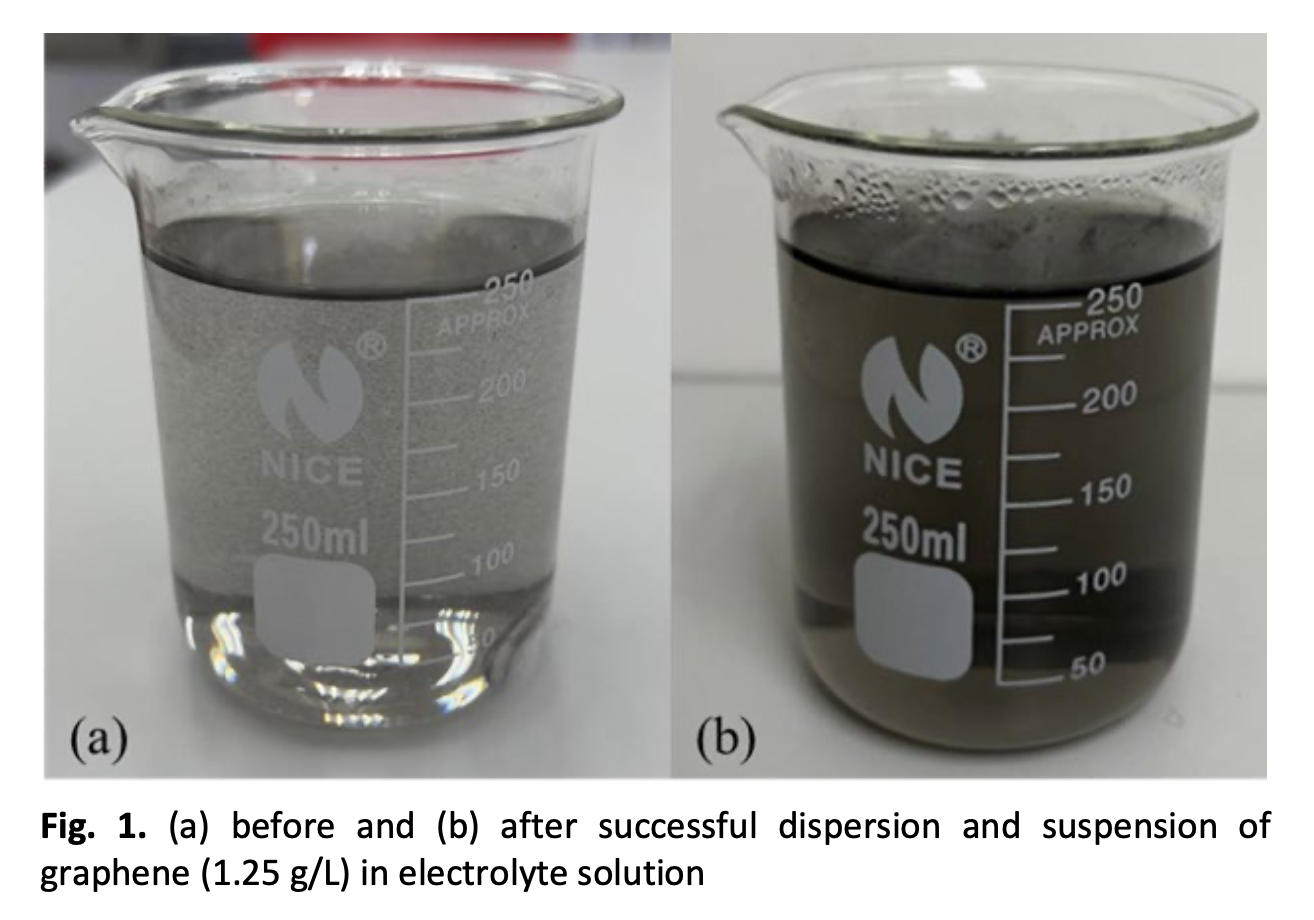
Thermoelectric films have become a prevalent research area due to their unique properties and potential applications in energy harvesting and waste heat recovery. Advancements in thermoelectric (TE) materials development have been highlighted for the improved self-powered micro-device applications. In this paper, a detailed process of electrodeposition Graphene/Bi2Te3 thermoelectric films by using a potentiostatic 3-electrode system is presented. An improved suspension and dispersion of graphene in the electrolyte solution (0.5-1.25 g/L graphene content) is prepared to attain better deposition of dispersed graphene in the nanocomposite film. The maximum deposition rate of the Graphene/Bi2Te3 films dropped more than half at 0.046 µm/min with 0.0185 A/dm2 recorded current density as compared to the pristine Bi2Te3. Up to 3 wt.% of well dispersed deposited graphene in the film have been successfully synthesized through -60mV pulsed deposition at room temperature. The average grain size of the Graphene/Bi2Te3 thermoelectric films decreased nearly 40% as compared to pristine Bi2Te3 film. This study found a smaller grain size and certain crystal defects formations for the synthesized nanocomposites. These could benefit thermoelectric properties by altering the electron mobility and phonons scattering.
Downloads