Poly(lactic acid)/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites: A Morphology Study and Mechanism of Reaction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.33.3.384392Keywords:
Poly(lactic acid), graphene oxide, poly(ethylene glycol), melt blendingAbstract
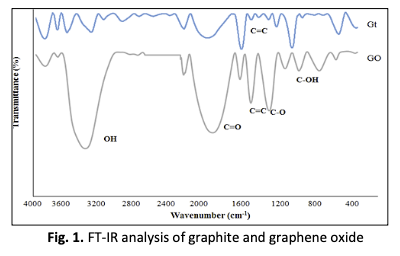
Because of environmental concerns, the use of biopolymer poly(lactic acid) (PLA) as a matrix has gotten a lot of attention. The graphite (Gt) was modified to produce graphene oxide (GO) using an acid treatment prior to mixing. The modified GO was validated by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) and Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy (UV-Vis) tests. Melt mixing produced PLA nanocomposites with 1.5 wt.% loadings of two distinct carbon-based materials, Gt and GO. The effect of a plasticizer of 5 wt.% poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) on nanocomposites was also investigated. The morphology study by Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) analysis showed the GO loading gave a smooth surface morphology as compared with PLA/Gt. These findings were identified by the presence of a smooth fracture surface, particularly when PEG was loaded, as an indication of good nanofiller spreading in the matrix. The mechanisms of reactions for Gt and GO dispersion in the PLA matrix were proposed to prove the morphology analysis.
Downloads