Student Profiling for Online Learning During Covid-19: A Systematic Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.34.2.5061Keywords:
Student profiling, online learning, Covid-19, Movement Control Command (MCO)Abstract
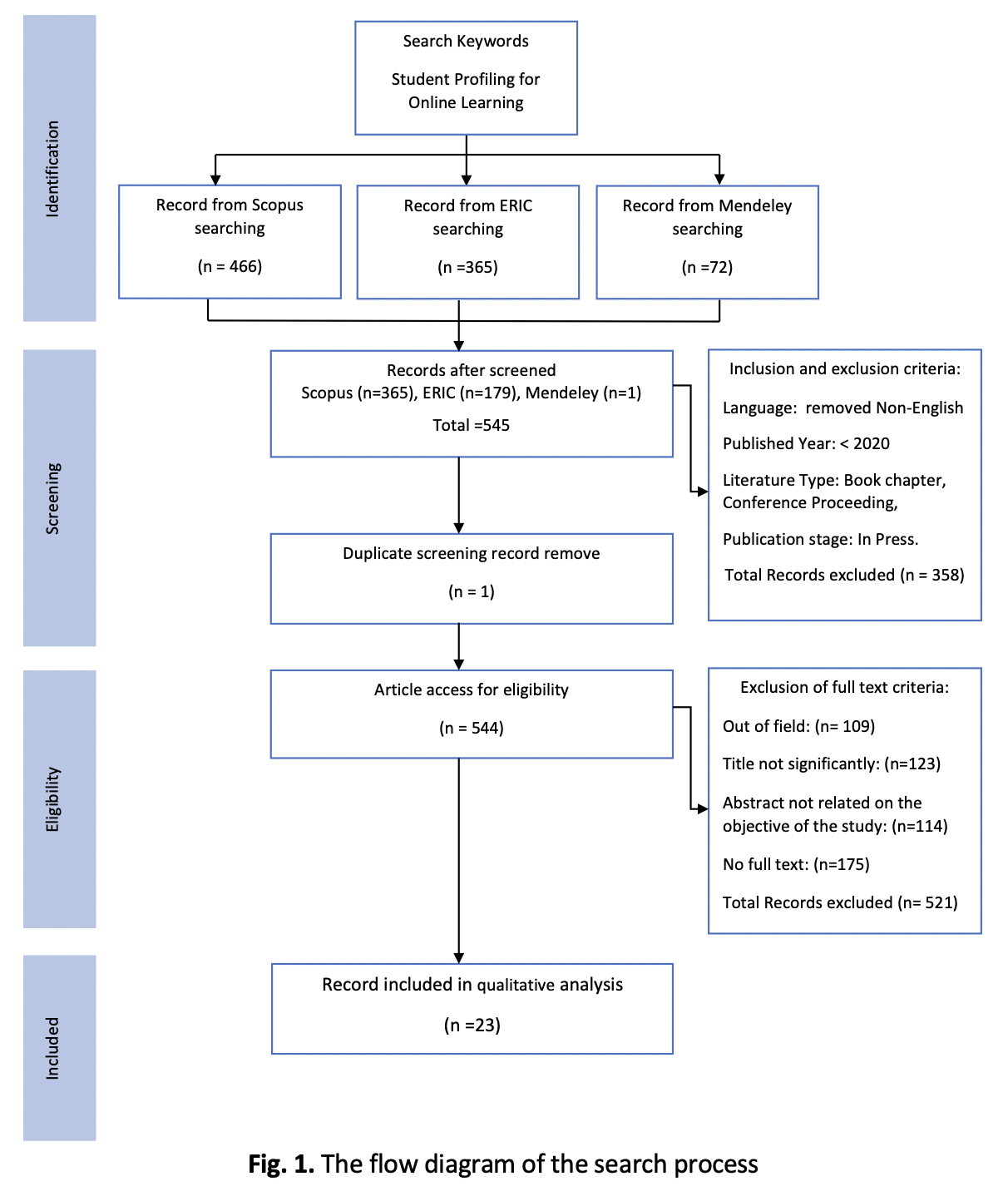
The Covid-19 epidemic has spurred significant changes in learning paradigms in several countries, including Malaysia. Particularly, the Malaysian government's Movement Control Order (MCO) forced both students and teachers to turn to online learning. It is true that its adoption is rife with fresh difficulties, including network coverage, device appropriateness, and socio-economic status of students, and digital competency, which makes teaching and learning at home incredibly difficult. Since students have a variety of learning needs, abilities, skills, and goals, it is crucial to develop learner profiles that can aid in the development of appropriate online learning approaches in order to address such issues. A systematic review of the most recent literature was conducted using three major databases: Scopus, ERIC, and Mendeley, as was envisioned in this context. The review helped identify 23 relevant publications that were then subjected to a thematic analysis, which helped reveal three (3) key themes for online learning: online platform, learner profile, and learning experience. It might be argued that understanding these thematic elements can assist teaching professionals in creating and putting into practice efficient online learning strategies for students of all educational levels. The results of this study emphasize the value of adopting student or learner profiles as a guideline to assist teaching practitioners in developing and implementing effective online teaching practices, which can ultimately make online learning sustainable long after the Covid-19 outbreak has passed.
Downloads