Effect of Steel Fibre Volume Fraction on Thermal Performance of Lightweight Foamed Mortar (LFM) at Ambient Temperature
Keywords:
Thermal performance, foamed concrete, lightweight, steel fibre, heat conductorAbstract
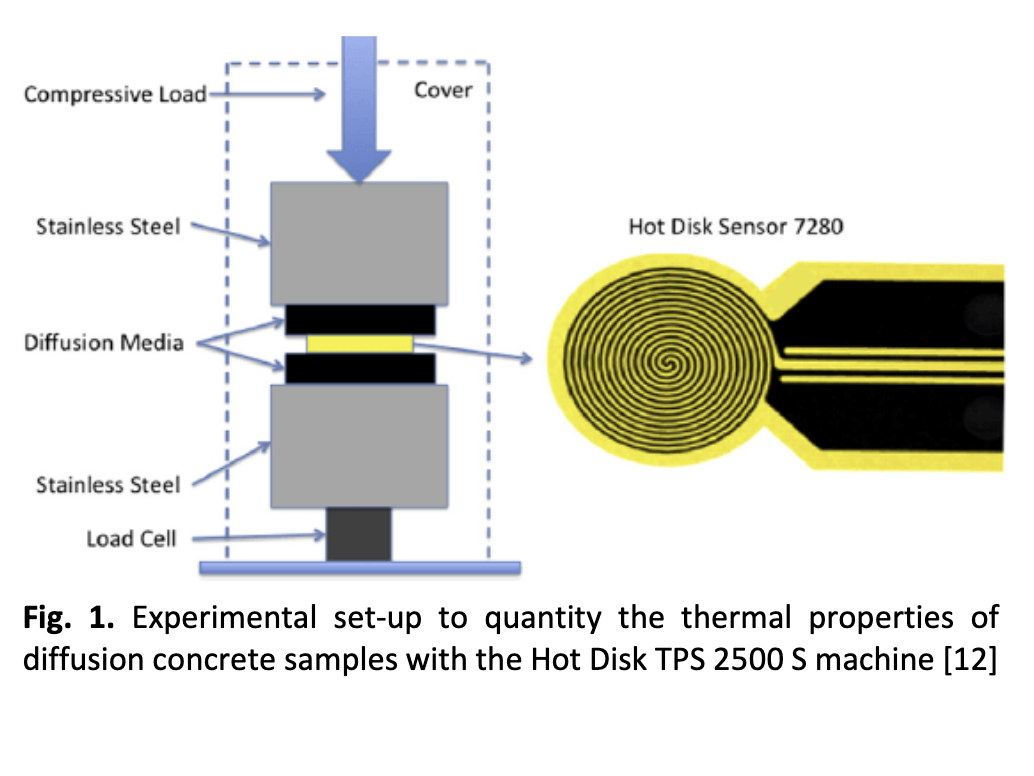
Lightweight foamed mortar (LFM) has grow into utmost commercial building material in the construction industry for non-structural and semi-structural applications owing to its reduced self-weight, flowability, stability and excellent thermal insulation properties. Hence, this study was conducted with the aims to develop an alternative for conventional concrete bricks and blocks for non-structural and semi-structural applications of masonry. Lightweight foamed mortar (LFM) is either a cement paste or mortar, relegated as lightweight concrete, in which suitable foaming agent entraps the air-voids in mortar. It therefore has a wide range of applications such as material for wall blocks or panels, floor & roof screeds, trench reinstatement, road foundations and voids filling. This research focuses on experimental investigation of thermal properties of LFM with inclusion of relatively low volume fraction (0.2% and 0.4%) of steel fibre at ambient temperature. There are three parameters will be scrutinized such as thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity as well as the specific heat capacity. There are two densities of 600kg/m3 and 1200kg/m3 had been cast and tested. The mix design proportion of LFM used for cement, aggregate and water ratio was 1: 1.5:0.45. The experimental results had indicated that the thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity and specific heat value slightly higher than control mix due to the addition of steel fibres. For instance, thermal conductivity, diffusivity and specific heat of 600 kg/m3 density control mix were 0.212W/mK, 0.477mm2/s and 545J/kg◦C respectively. When 0.2% volume fraction of steel fiber was added in the mix of 600 kg/m3 density, the value of thermal conductivity, diffusivity and specific heat were increased to 0.235W/mK, 0.583mm2/s and 578J/kg◦C correspondingly. This is due to the characteristic of the steel fibre application in which steel fibre is good as heat conductor and excellent in absorbing heat. Therefore there is a potential of utilizing steel fiber in cement based material like LFM for components that needs excellent heat absorption capacity.
Downloads