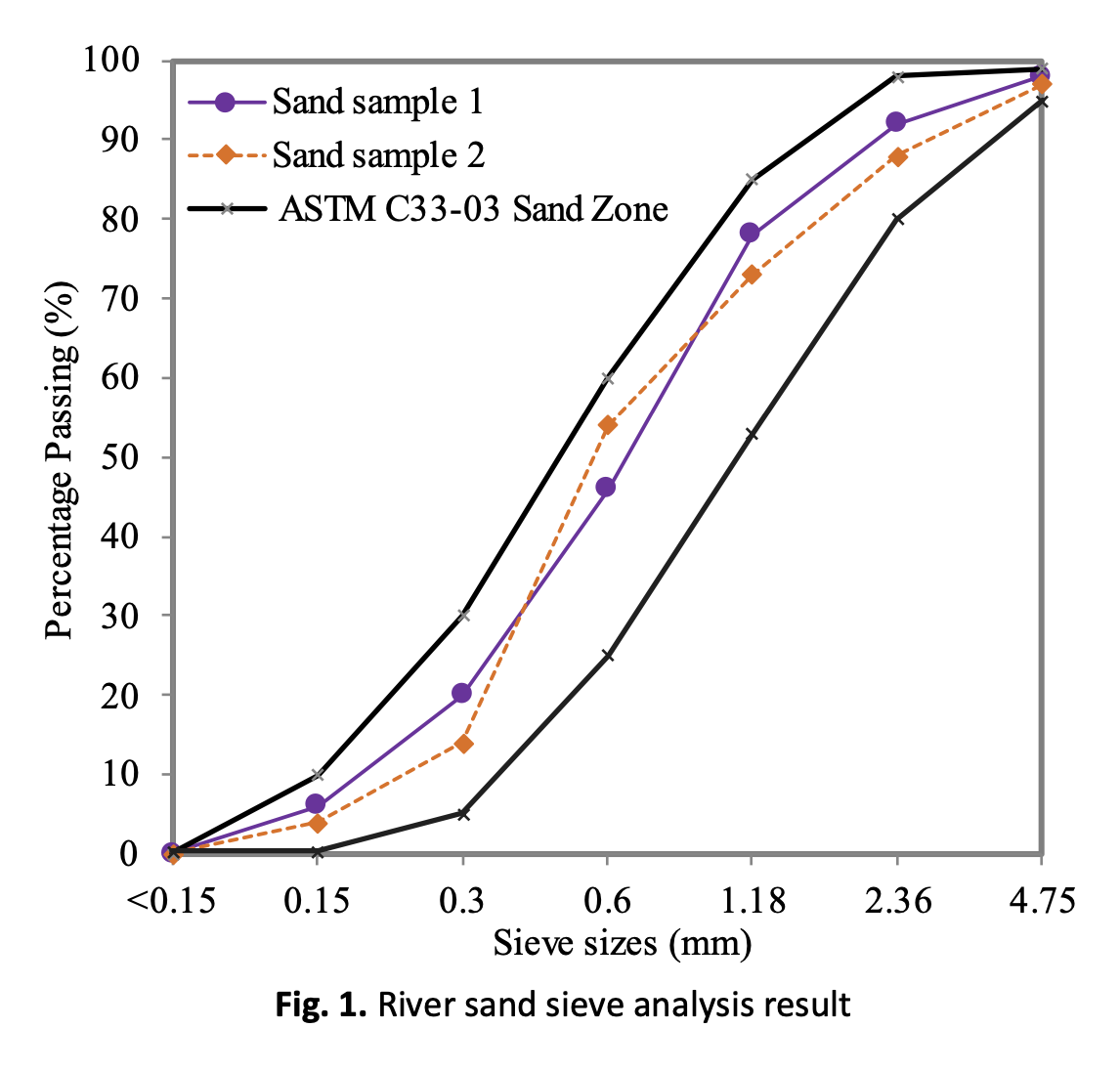
The Influence of Pulverized Fuel Ash (PFA) on the Thermal and Transport Properties of Foamed Concrete
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.108.2.1730Keywords:
Foamed concrete, thermal conductivity, diffusivity, permeable porosity, water absorptionAbstract
The incorporation of materials derived from industrial waste presents a viable avenue for mitigating the exorbitant production expenses associated with building materials, while concurrently ameliorating the deleterious ecological ramifications of said waste. The utilization of pulverized fuel ash (PFA), an industrial residue resulting from the combustion of powdered coal in an electricity-generating facility, as a substitute for cement in the composition of concrete, is a viable option owing to its inherent pozzolanic properties. The present study endeavours to investigate the potential of Partially-Fumed Ash (PFA) as a viable substitute for cement in the production of foamed concrete (FC). The thermal and transport properties were meticulously assessed, with a particular focus on thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, specific heat capacity, water absorption, and porosity. A series of experiments have been undertaken wherein varying proportions of Portland Pozzolan Cement have been substituted for PFA, specifically at levels of 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, and 50% by weight. The findings suggest a prospective application of PFA in the manufacturing of FC. The utilization of PFA (Pulverised Fuel Ash) assumes a pivotal role in enhancing the thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, specific heat capacity, water absorption, and porosity of FC. Therefore, it can be inferred that the utilization of PFA holds promising potential in the production of cost-effective, lightweight construction materials, while simultaneously mitigating the adverse environmental consequences.
Downloads