Numerical Computational of Blood Flow and Mass Transport in Stenosed Bifurcated Artery
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.110.2.7994Keywords:
Blood Flow, Mass Transfer, Stenosis, Bifurcated Artery, Carreau Fluid Model, COMSOL MultiphysicsAbstract
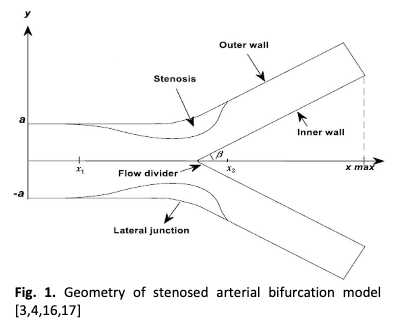
Stenosis refers to the narrowing of blood vessels caused by atherosclerosis, which can lead to serious circulatory problems by obstructing blood flow and mass transfer to other organs and tissues in the body. The objective of this investigation is to numerically examine the mass transfer of blood flow in a stenosed bifurcated artery using COMSOL Multiphysics, based on the finite element method. The study takes into account the geometry of a bifurcated artery with stenosis present at the mother and daughter arteries. The blood vessel is modeled as a two-dimensional (2D) rigid wall, and the blood flow is assumed to follow a non-Newtonian Carreau fluid model, being incompressible, laminar, and steady. The continuity equation, momentum equation, and mass transfer equation, along with boundary conditions, will be solved using COMSOL Multiphysics based on the finite element method. The simulation results show that the formation of recirculation zones, as indicated by streamline patterns and mass concentration, can significantly impact the severity of stenosis and Reynolds numbers. Thus, individuals exposed to such recirculation zones may be at risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Downloads