Unsteady MHD Stagnation Point Flow of Al2O3-Cu/H2O Hybrid Nanofluid Past a Convectively Heated Permeable Stretching/Shrinking Sheet with Suction/Injection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.96.1.96114Keywords:
Hybrid nanofluid, unsteady stagnation-point, suction/injection, magnetohydrodynamic (MHD), bvp4cAbstract
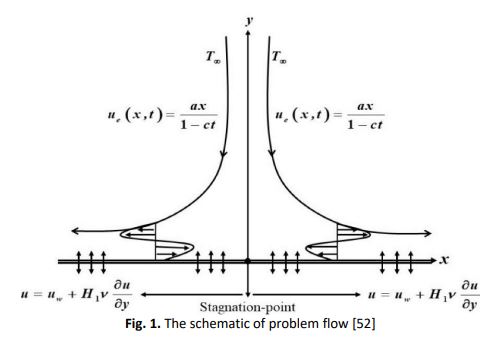
The numerical investigation of unsteady magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) stagnation point flow of Al2O3-Cu/H2O hybrid nanofluid past a convectively heated permeable stretching/shrinking sheet with suction/injection effect is underlined. The characteristic of MHD and boundary condition with suction/injection has received a lot of consideration due to its across-the-board application in mechanical and chemical engineering. The governing continuity, momentum and energy equations are transformed into a system of nonlinear ordinary differential equations using similarity transformation, which is then solved using the bvp4c routine. Numerical results are obtained for the skin friction coefficient, local Nusselt number as well as the velocity and temperature profiles for certain values of the governing parameters, namely suction/injection parameter, copper nanoparticle volume fraction parameter and MHD parameter. Results showed that both velocity profile and temperature increase as the suction/injection parameter increases for the first solution and decreases for the second solution. Similarly, when increase the value of MHD parameter M, the velocity and temperature profiles are decreases for both solutions. The magnitude of the reduced skin friction coefficient and the local Nusselt number are notably increased for the first solution with increasing values of the suction/injection and MHD parameters. Finding also revealed that the skin friction coefficient is intensified in conjunction with the local Nussel number by adding up the copper nanoparticle volume fraction. In general, dual solutions are found to exist to a particular extent of the stretching/shrinking sheet.
Downloads