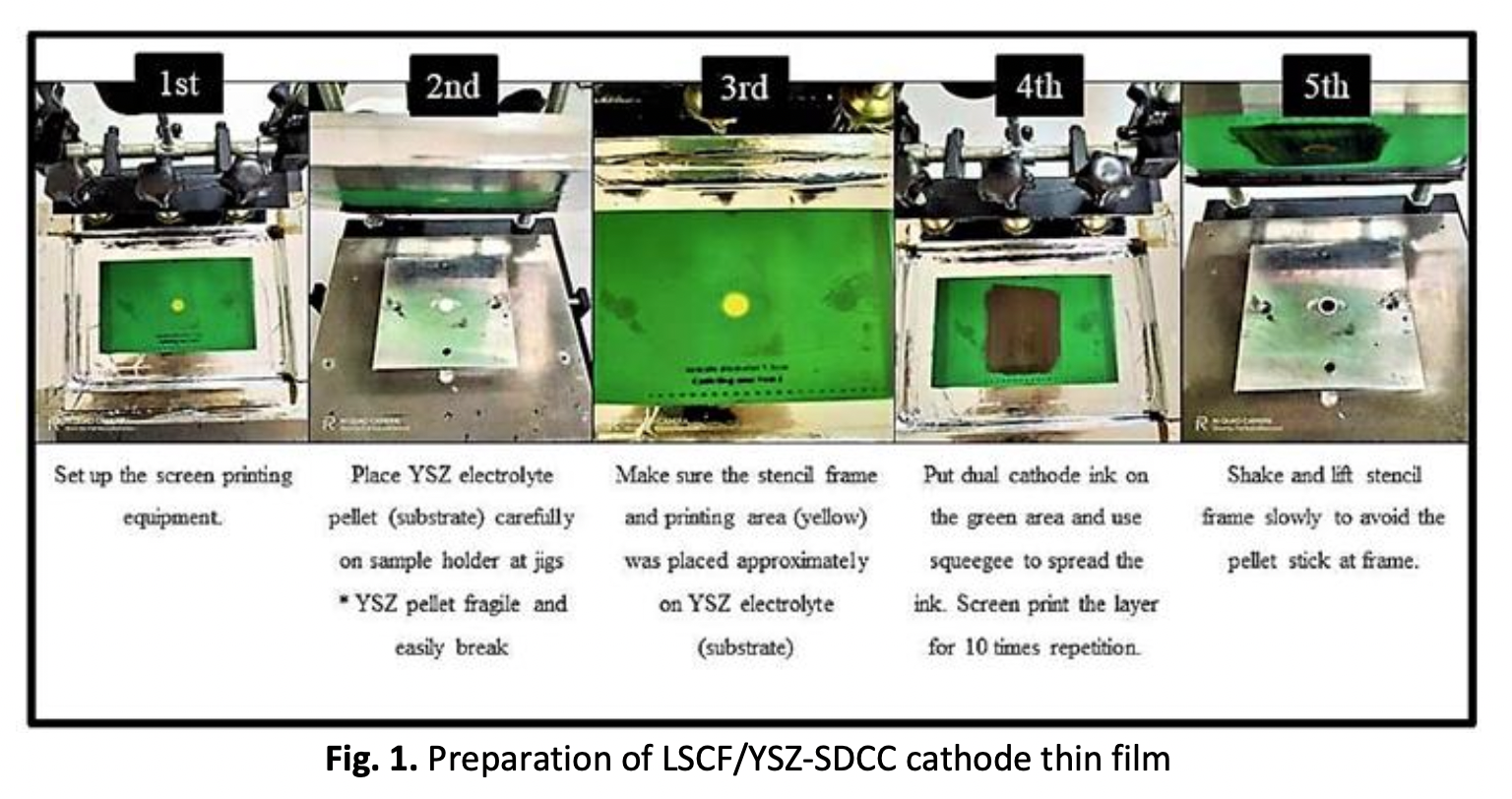
An Approach to the Development of LSCF/YSZ-SDCC Dual Composite Cathodes for Intermediate Temperature SOFCs
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aram.108.1.98110Keywords:
Cathode, Dual Composite, ITSOFC, LSCF, Screen Printing, YSZ-SDCCAbstract
A development of dual composite cathode, La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-d/Y2ZrO5-Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9 carbonate (LSCF/YSZ-SDCC) has been studied subjected on the composition of YSZ-SDCC composite. LSCF/YSZ-SDCC dual composite powders were produced through the high-energy ball milling method with a varied composition of YSZ-SDCC composite powder (50-70 wt.% YSZ: 50- 30 wt.% SDCC). The calcined LSCF/YSZ-SDCC powders were then successfully screen-printed on YSZ pellet to form a cathode thin film. A complete symmetrical cell was sintered for 90 minutes at 600°C. The crystalline phase, the carbonate bonding and the physical morphologies of the YSZ-SDCC composite cathode powders and the LSCF/YSZ-SDCC dual composite cathode powders were investigated. Furthermore, the microstructure and cathode thin film properties including electrochemical performances of LSCF/YSZ-SDCC were all evaluated. The various processes did not affect the carbonate bonding in any of the samples, however, phase identification analysis revealed the appearance of strontium carbonate (SrCO3) as the secondary phase in the calcined LSCF/YSZ-SDCC powders. The microstructure study of the particles after milling demonstrates that the particles for all three YSZ-SDCC compositions do not agglomerate, with grain sizes of 244.97 40.66, 213.47 41.63, and 173.27 25.83 nm, respectively. Following that, all samples were electrochemically analyzed at temperatures of 700°C, 600°C, and 500°C. As compared to the other combinations, LSCF/YSZ-SDCC with 50:50 wt.% YSZ-SDCC compositions co-fired at 700°C showed the most favourable value in this study.
Downloads